Full Length Research Article - (2023) Volume 18, Issue 5
Principal Leadership Effectiveness A Literature Review
Hardianto1*, Hidayat2, Zulkifli3 and Muhammad Nurhsyam Ali Setiawan4*Correspondence: Hardianto, Department of Social Science Education, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Pasir Pengaraian, Rokan Hulu, Indonesia, Email:
Department of Management, Faculty of Economic, Universitas Pasir Pengaraian, Rokan Hulu, Indonesia
2Department of Law, Faculty of Law, Universitas Pasir Pengaraian, Rokan Hulu, Indonesia
3Sports and Health Education Study Program, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Pasir Pengaraian, Rokan Hulu, Indonesia
Received: 06-Oct-2023 Published: 20-Oct-2023
Abstract
Effective school principal leadership is necessary to make school goals optimally achieved. This research uses the library method. Data collection was carried out with the help of the Google Scholar search engine using the keywords "principal leadership" and "principal leadership style". Based on the results of the study it was concluded that transformative, authoritarian, democratic and situational leadership styles have a positive effect on teacher performance. Meanwhile, transactional, task-oriented, bureaucratic and charismatic leadership styles have a negative effect on teacher performance. To generate teacher motivation, principals can provide rewards, career advancement opportunities, create a family atmosphere, create open communication, provide trust, provide space for innovation and provide exemplary. The effectiveness of the principal's leadership in terms of handling conflict is by taking preventive and curative actions.
Keywords
Effectiveness. Leadership. Principal
Introduction
Schools are educational institutions designed to produce quality generations of the nation. The progress of a nation is largely determined by the quality of education. People with advanced education will find it easier to face global challenges. Educated people will also be better able to counteract the negative effects of technological advances. Conversely, countries with underdeveloped education have low competitiveness (Hardianto, 2019a). To realize a quality school requires a quality headmaster. The school principal plays a very important role in realizing educational goals (Hardianto et al., 2022).
The principal is a chosen person who knows the condition of the school he leads. Understanding of the state of the school environment is needed in making the right decision. The accuracy of the principal in making decisions will make his leadership effective. Leadership is a process of one's activities to move others by leading, guiding, influencing others to do something in order to achieve the expected results (Sutrisno, 2014). Principal leadership is the principal's ability to mobilize teachers and education staff so that they are able to carry out activities in achieving school goals.
Becoming an effective school principal is necessary in facing increasingly difficult challenges. Technological advances are getting faster and the new normal era after Covid 19 also needs to be considered by school principals. Currently a new breakthrough is needed so that the quality of education is getting better. Therefore, accuracy is needed in choosing a school principal figure.
Mistakes in selecting school principals will have a negative impact on school progress. The negative impact is the ineffective leadership of the school principal. Therefore, it is necessary to recruit school principals in accordance with applicable regulations (Hardianto et al., 2022). Principals who are not qualified will fail in leading the school to achieve its goals. The failure of the principal makes his leadership ineffective. Ineffective school principal leadership will of course harm students, teachers and also education staff in realizing their hopes.
Currently there are not many articles that discuss the effectiveness of school principal leadership. The effectiveness of leadership that is studied looks more at the figure of corporate leadership. School leadership is of course different from corporate leadership. Schools are organizations that are not financially profit oriented but are oriented towards providing educational services. The effectiveness of the principal's leadership is very important in order to achieve optimal educational goals.
Basically, the effectiveness of the principal's leadership can be seen from various factors. In this article, the author will look at leadership styles, how to motivate subordinates and resolve conflicts. These three factors attract the writer's attention, because every school principal basically has a different style of leadership. Every teacher, student and education staff also has a desire to be led by the principal in a different style.
Every teacher and education staff has a different way of motivating themselves. The principal is expected to be an extrinsic motivator for teachers. The principal's ability to motivate teachers is very important. Teachers who have high motivation in work will be more accomplished in their work. This article will present the principal's way of arousing teacher motivation.
Conflict at school is certainly impossible to avoid. Conflicts can occur between school principals and teachers, between fellow teachers or between teachers and education staff. Unresolved conflicts certainly have a negative impact on schools. Therefore, it is necessary to have a school principal who is able to handle conflicts well. This article will also discuss how school principals deal effectively with conflict. The formulation of the problem in this study is as follows:
1. How is the effectiveness of the principal's leadership in terms of leadership style?
2. How effective is the principal's leadership in motivating subordinates?
3. How effective is the principal's leadership in dealing with conflict?
Method
This study uses library research methods. The literature review method is collecting data by understanding and studying theories from the literature related to research (Zed, 2008). In this study, the main data source is articles published in national journals. The search was carried out using the Google Scholar search engine. The articles used are articles published from 2019 to 2022. The keywords used are principal leadership and school principal leadership style. In this study, 44 articles were collected. Data analysis was carried out using content and descriptive analysis (Fadli, 2021). Presentation of data is done deductively.
Results and discussion
Effectiveness of the principal’s leadership in terms of leadership style
An effective leader is a leader who is able to achieve organizational goals. Effective principal leadership will be able to realize school goals optimally. School goals will be realized when the teacher as the spearhead of learning activities has high performance. The role of the principal is very important in optimizing teacher performance. Principal leadership positively influences teacher performance (Elazhari et al., 2021), (Frismelly et al., 2021), (Sukiyanto & Maulidah, 2020), (Jaya, 2021), (Handayani et al., 2020), (Indajang et al., 2020), (Azis & Suwatno, 2019), (Sulfemi, 2020), (Kartini et al., 2020), (Darmawan, 2019), (Jaliah et al., 2020) and (Hardianto, 2015b). This means that the better the leadership applied by the school principal, the better the teacher's performance will be.
In achieving goals, the principal certainly applies a certain leadership style. A school principal will not use just one leadership style while carrying out his leadership activities. The principal's preferred leadership style will make the work atmosphere better (Hardianto, 2015b). Teachers who have different characteristics want different treatment from the principal (Zuldesiah et al., 2021). When the working atmosphere is good, of course work success will be more easily achieved.
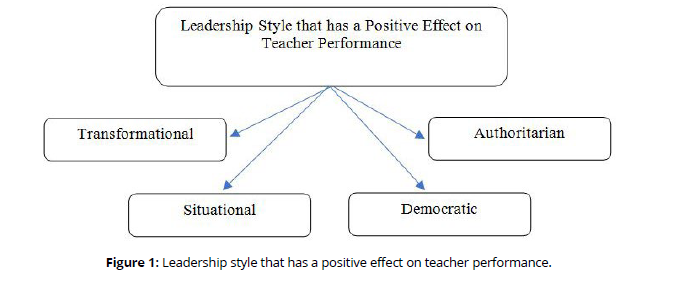
When viewed from the leadership style, the research results show that the transformational leadership style positively affects teacher performance (Rokhani, 2020) and (Taufik, 2019). Democratic leadership style also positively influences teacher performance (Rokhani, 2020) and (Rosaliawati et al., 2020). Situational (Zulfiter et al., 2020) and authoritarian (Rokhani, 2020) leadership styles also positively influence teacher performance. In addition to teacher performance, the principal's leadership style also influences the performance of school operators (Zulfan et al., 2021).Based on the research results; it is known that the leadership style that influences the performance of teachers and educational staff positively is a transformational, democratic, situational and authoritarian leadership style. The following describes a leadership style that positively influences teacher performance (Figure 1).
Of the four leadership styles that have a positive effect on teacher performance, the transformational style is more common. The transformational leadership style in addition to improving teacher performance also improves the quality of education (Bunbababan et al., 2022). Principals with a transformational style will be able to accommodate the needs of their subordinates at a higher level than what they need (Fadhilah et al., 2020). The school principal's transformational style can increase teacher achievement motivation (Nazayanti et al., 2019). Principals with a transformational style are able to solve problems innovatively and are committed to the vision (Wote & Patalatu, 2019). The principal's transformational style can also shape character (Syarifah, 2019).
Another interesting thing was found that teacher competence can weaken the effect of leadership style on performance (Indajang et al., 2020). Teachers with low competence will not be able to display high performance even though they are led by a quality principal. There needs to be a competency qualification standard owned by the teacher. Teachers in Indonesia must have four competencies, namely pedagogic, professional, social and personality.
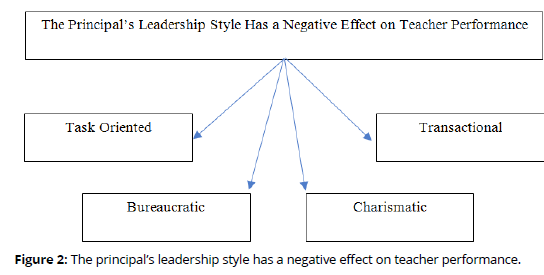
Different results were actually obtained from Rachmawati Aziizah research which stated that leadership had a negative effect on teacher performance (Rachmawati Aziizah, 2018). The leadership style studied is a task-oriented leadership style. This means that the more the principal applies a taskoriented leadership style, the lower the teacher's performance. A task-oriented leadership style is a work-oriented leadership style, paying more attention to completing work with very strict supervision so that tasks are completed according to their wishes (Yanti, 2022). Principals who put more emphasis on assignments can cause teachers to be pressured at work. Teachers who are stressed at work will not be able to display maximum performance.
In addition to task-oriented leadership styles, bureaucratic, charismatic and transactional leadership styles negatively affect teacher performance (Rokhani, 2020). The bureaucratic style is a leadership style characterized by the strict implementation of procedures that apply rigidly and no more flexibility (Haryani et al., 2022). Charismatic leadership style is a leadership style in which subordinates are fully dependent on the leader, when the leader leaves the organization the organization will lose direction (Rokhani, 2020). Transactional leadership style is a leadership style that involves an exchange process between leaders and subordinates by promising subordinates will receive rewards if they are able to complete mutually agreed tasks (Putranti & Harianti, 2022). The results of this study mean that principals who are increasingly bureaucratic, charismatic or transactional will reduce teacher performance. The following describes four principal leadership styles that have a negative effect on teacher performance (Figure 2).
Besides having an influence on teacher performance, the principal's leadership style also contributes to teacher performance (Zuldesiah et al., 2021), (Ratmini et al., 2019). In addition, leadership style is related to teacher performance (Gusman, 2014) and (Rosaliawati et al., 2020). Relationship means showing the degree of closeness between the two variables studied, while influence is used to see the pattern of causality from one variable to another.
The effectiveness of principal’s leadership in motivating teachers
Effective school principal leadership is one that can realize school goals properly. In realizing the goal required teachers who have high work motivation. The principal must be able to motivate teachers and education staff to work diligently. Working with high motivation will make the teacher more successful at work. Principals need to motivate teachers to work so that goals can be achieved (Yeni & Nellitawati, 2018).
Principal leadership has an impact on teacher work motivation (Solihin et al., 2021) and (Hardianto, 2015a). The principal can be an extrinsic motivator for teachers. Teachers who have high work motivation will be more enthusiastic at work. Providing motivation from school principals has a positive impact, especially in developing interest and teacher performance activities (Marce et al., 2020). Teachers who have high work motivation will be able to carry out difficult tasks well.
The principal's leadership style influences teacher performance (Sukiyanto & Maulidah, 2020) and (Rosid & Mukarromah, 2020). Based on research findings, it is known that consultative leadership style can increase teacher work motivation (Frismelly et al., 2021) and (Hartawan, 2020). The consultative leadership style includes providing support, guidance and work examples by the leadership (Hariansyah et al., 2022). In addition, the participative leadership style also increases the teacher's work motivation (Hartawan, 2020). Participatory leadership style is a leadership style that involves subordinates in making decisions (Habi et al., 2022). Therefore, to increase teacher motivation, principals can apply a consultative style and a participatory style.
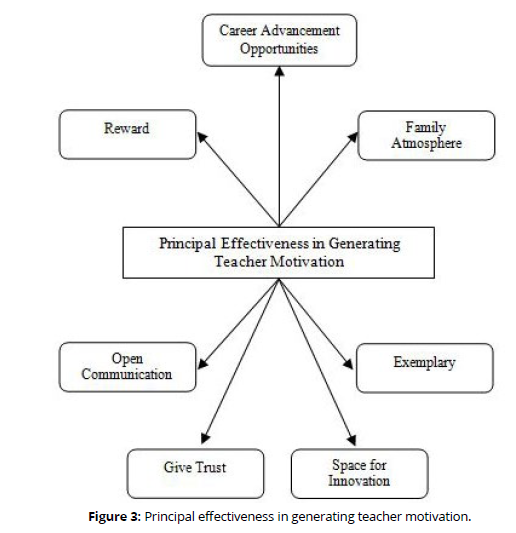
Apart from being seen from the leadership style, efforts to increase teacher motivation can be carried out by the principal by giving rewards (Hartawan, 2020), (Zulfiter et al., 2020), (Elazhari et al., 2021), (Fatikah & Fildayanti, 2019) and (Hardianto, 2019b). Rewards can be given in the form of money, certificates or other objects. Teacher motivation can also be increased by providing career advancement opportunities (Elazhari et al., 2021), (Wisda, 2021) and (Fatikah & Fildayanti, 2019). Principals should provide opportunities for teachers to continue their education or attend teacher training.
Principals can also increase teacher motivation by creating a family atmosphere and open communication (Zulfiter et al., 2020) and (Hardianto, 2018). Open communication allows the teacher to convey whatever is felt to the principal, so that the problem felt by the teacher can be known by the principal to find a solution. Teacher motivation will also grow with the trust given by the principal (Elazhari et al., 2021).
Principals can increase teacher motivation by providing space for innovation (Hartawan, 2020). Advances in technology allow teachers to innovate in teaching. Teachers should be given broad opportunities to innovate in teaching. The use of social media that students like can be used by teachers in delivering teaching material. Teacher motivation can also be generated by setting an example (Hardianto, 2015b). The principal should be an exemplary figure who can be used as an example by all school members.
The efforts of the principal in arousing teacher motivation can be described as follows (Figure 3).
Citation of other works should be made to avoid plagiarism. When referring to a reference item, please use the reference number as in (Kleij, 2019) or (Brockett & Hiemstra, 2020) for multiple references. The use of “Ref (Hiemstra & Brockett, 2012)...” should be employed for any reference citation at the beginning of sentence. For any reference with more than 3 or more authors, only the first author is to be written followed by et al. (e.g. in (Geng et al., 2019)). Examples of reference items of different categories shown in the References section. Each item in the references section should be typed using 8 pt font size (Creswell & Clark, 2011; Fraenkel et al., 2012; Honey & Marshall, 2003; Ismayilova & M.Klassen, 2019; Krueger & Casey, 2015; Mahvelati, 2021).
Effectiveness of principal’s in dealing with organizational conflict Leadership effectiveness is also determined by how the principal can handle conflicts that occur. Not all conflicts have a negative impact on schools (Latinapa et al., 2021). Conflict can lead to competition thereby triggering high performance. For conflict to have a positive impact on schools, it takes a school principal who can handle conflict well.
In an organization organizational conflict is always there. Likewise at school, there will always be conflicts that occur. Conflicts can occur on a small or large scale. Principals must have skills in dealing with conflict (Nasrudin et al., 2019). Conflict handling skills contribute to improving teacher performance (Nugroho, 2020). In addition to dealing with conflicts that have occurred, efforts to minimize potential conflicts must also be the concern of the school principal. Small conflicts if left unchecked can become big conflicts. For this reason, when a conflict is seen, the principal must immediately deal with it.
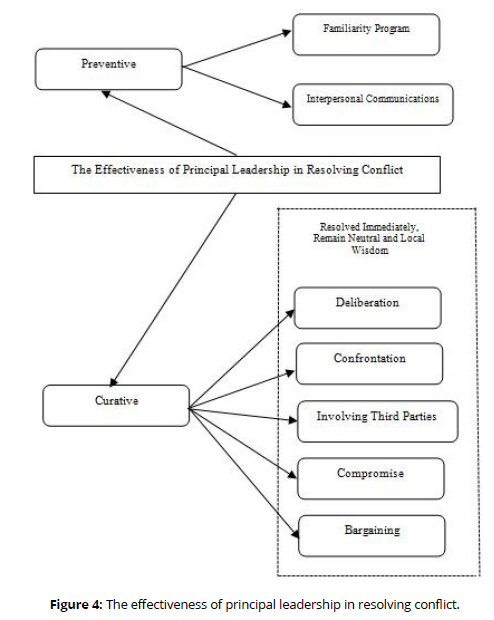
Efforts to prevent conflict need to be the concern of the school principal. Principals need to take preventive action to prevent conflicts from arising. Efforts that can be made such as implementing a familiarity program (Mufti et al., 2021). When the atmosphere among school members is harmonious, of course the potential for conflict to arise can be minimized. Efforts that can be made by school principals to prevent conflicts from occurring are to provide a common understanding regarding the policies and regulations that apply in schools (Andani et al., 2022). Misunderstanding of rules and policies can lead to conflict. Providing understanding is done by conducting interpersonal communication (Latinapa et al., 2021).
When a conflict has occurred, the principal needs to deal with it immediately. One of the principal's efforts in dealing with conflict is to provide direction (H Bay & W. Dj. Pomalato, 2021). Briefing is a communication made by the school principal to those in conflict to provide an explanation of the problems that occur. In dealing with conflicts, school principals must be neutral, given conflicting opportunities to express their opinions, focus on increasing competence and responsibility (Ernaliza et al., 2020). When there are parties who feel the principal is not being neutral, it will be difficult to resolve the conflict. In addition, the principal's leadership style influences conflict control (Latinapa et al., 2021).
Principals can handle conflicts by deliberation, involving third parties, confrontation, compromise, and bargaining (Nasrudin et al., 2019). Involve a third party, namely finding another person who is believed to be neutral in helping to resolve the conflict. Efforts to deal with conflict need to pay attention to local wisdom (Az-Zahra et al., 2019). Local wisdom which can be in the form of culture, customs and habits or values owned by the people of a region must be considered in overcoming conflicts that occur.
Based on research findings to see the effectiveness of the principal's leadership in overcoming conflict can be seen preventively and curatively. Prevention of the emergence of conflict (preventive) is done by building interpersonal communication and familiarity activities. When the conflict has occurred (curative) then the principal must immediately resolve the conflict, be neutral and look at local wisdom. The way to resolve conflicts is by deliberation, confrontation, involving third parties, compromise and bargaining. To explain more, it will be described below (Figure 4).
Conclusion
Based on the discussion above, it can be concluded that transformational, situational, democratic and authoritarian leadership styles have a positive effect on teacher performance. Task-oriented leadership style, bureaucratic style, charismatic style, and transactional style have a negative effect on teacher performance. Efforts by the principal in arousing teacher motivation can be carried out by giving awards, providing career advancement opportunities, creating a family atmosphere, creating open communication, providing trust, providing space for innovation, and setting an example. The principal's efforts in dealing with conflict can be seen preventively and curatively. Preventively carried out by holding familiarity events and creating good interpersonal communication. Curatively it can be done by deliberation, confrontation, involving third parties, compromise and bargaining.
It is suggested that school principals should apply more transformational, democratic, situational styles in leading their schools. If necessary, the application of an authoritarian style can also be done because it has a positive effect on teacher performance. The principal is expected to be able to act as an extrinsic motivator for teachers by giving awards, creating a family atmosphere and also a space for innovation for teachers. Principals should prevent conflict. If a conflict occurs, it needs to be resolved immediately by taking into account local wisdom.
This research has limitations because it looks at problems from every level of education. Each level of education certainly has its own characteristics. It is hoped that further research will carry out more specific research at a certain level of education.
Acknowledgements:
Acknowledgments to the head of the social educational program at Pasir Pengaraian University for providing moral support in writing this article.
References
Andani, M., Setiawan, F., Azizah, R. H., Kurniawan, D. S., & Rahman, P. (2022). Managemen Konflik (Upaya Penyelesaian Konflik Dalam Organisasi Sekolah Di SMP Muhammadiyah Al-Manar Boarding School). Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan Al Hadi, 2(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.31602/jmpd.v2i1.6326
Azis, A. Q., & Suwatno, S. (2019). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru di SMK Negeri 11 Bandung. Jurnal Pendidikan Manajemen Perkantoran, 4(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.17509/jpm.v4i2.18020
Az-Zahra, R., Martunis, & Abd, D. (2019). Efektifitas Layanan Mediasi dalam Mengatasi Konflik Antar Siswa di SMAN 1 dengan SMKN 2 Langsa. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Bimbingan Dan Konseling, 4(4), 46–52.
Brockett, R. G., & Hiemstra, R. (2020). Self-direction in adult learning: Perspectives on theory, research, and practice. Routledge.
Bunbababan, Y. S., Iriani, A., & Waruwu, M. (2022). Evaluasi Kepemimpinan Transformasional Kepala Sekolah Dalam Meningkatkan Mutu Pendidikan dengan Menggunakan Model CIPP. Kelola, 9(2), 223–237.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2011). Choosing a mixed methods design. In Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research (pp. 53–106). Sage Publications, Inc.
Darmawan, A. (2019). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Budaya Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru (Studi pada SMK Rumpun Pariwisata di Kota Tangerang). Jurnal Mandiri : Ilmu Pengetahuan, Seni, Dan Teknologi, 3(2), 244–256.
Elazhari, Tampubolon, K., Barham, & Parinduri, R. Y. (2021). Pengaruh Motivasi dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru di SMP Negeri 2 Tanjung Balai. All Fields of Science J-LAS, 1(1), 44–53.
Ernaliza, E., Fitria, H., & Fitiani, Y. (2020). Peranan Manajerial Kepala Sekolah dalam Mengatasi Konflik Guru. Journal of Education Research, 1(3), 245–250. https://doi.org/10.37985/jer.v1i3.28
Fadhilah, M. L. Z., Suryadi, & Abubakar. (2020). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Transformasional Kepala Sekolah terhadap Etos Kerja Guru dan Staf. Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan, 2(2), 206–224.
Fadli, M. R. (2021). Memahami Desain Metode Penelitian Kualitatif. Jurnal Humanika, 21(1), 33–54.
Fatikah, N., & Fildayanti. (2019). Strategi Kepala Sekolah Dalam Peningkatan Motivasi Dan Etos Kerja Guru Di SMA Negeri Bareng Jombang. IJIES: Indonesian Journal of Islamic Education, 2(2), 167–182.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., & Hyun, H. H. (2012). How to design and evaluate research in education. McGraw-Hill.
Frismelly, A., Giatman, M., & Ernawati. (2021). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru. Jurnal Dirasah, 4(2), 81–88. https://doi.org/10.33753/mandiri.v3i2.85
Geng, S., Law, K. M. Y., & Niu, B. (2019). Investigating self-directed learning and technology readiness in blending learning environment. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(17), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0147-0
Gusman, H. E. (2014). Hubungan Gaya Kepemimpinan dengan Kinerja Guru di SMP N Kecamatan Palembayan Kabupaten Agam. Bahana Manajemen Pendidikan, 2(1), 293–301.
H Bay, I., & W. Dj. Pomalato, S. (2021). Perilaku Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Di SMA Negeri 1 Lemito. Berajah Journal, 2(1), 104–110. https://doi.org/10.47353/bj.v2i1.60
Habi, R. A. S., Alam, H. V., & Asi, L. L. (2022). Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Partisipatif Terhadap Perilaku Kerja Pegawai Pada Dinas Penanaman Modal ESDM dan Transmigrasi Provinsi Gorotalo. Jambura, 5(2), 498–503.
Handayani, E., Lian, B., & Rohana, R. (2020). Kinerja Guru Ditinjau Dari Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi Dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah. JMKSP (Jurnal Manajemen, Kepemimpinan, Dan Supervisi Pendidikan), 6(1). https://doi.org/10.31851/jmksp.v6i1.3981
Hardianto. (2015a). Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Untuk Meningkatkan Motivasi Kerja Guru Ditinjau Dari Perspektif Agama Islam. Hikmah: Jurnal Pendidikan Agama Islam, 5(1), 45–62.
Hardianto. (2015b). Kontribusi Motivasi Berprestasi dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Terhadap Kinerja Dosen FKIP UPP. Edu Research, 4(1), 43–52.
Hardianto. (2018). Optimalisasi Kepuasan Kerja Guru. Kelola: Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan, 5(2). https://doi.org/10.24246/j.jk.2018.v5.i2.p190-195
Hardianto. (2019a). Conducting Quality Culture in Educational Institutions. Journal Peuradeun, 7(2), 257–268.
Hardianto. (2019b). Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi, Penghargaan dan Kepercayaan Terhadap Motivasi Berprestasi Pegawai Dinas Pendidikan Pemuda dan Olahraga Kabupaten Rokan Hulu. JAMP: Jurnal Akuntabilitas Manajemen Pendidikan, 6(2), 193–203.
Hardianto, H., Aida, W., & Sari, V. P. (2022). Factors Affecting and Affected by Principal Leadership Effectiveness: A Systematic Literature Review. Jurnal Pendidikan Progresif, 12(3), 1008–1020.
Hariansyah, Wahyudi, & Radiana, U. (2022). Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Instruktif, Konsultatif, Partisipatif dan Delegatif Terhadap Produktivitas Kerja Guru SMA Negeri Sambas. Jurnal Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran Khatulistiwa, 11(6), 407–420.
Hartawan, H. A. (2020). Meningkatkan Motivasi Kinerja Guru Melalui Kepala Sekolah. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Profesi Guru, 3(2), 386. https://doi.org/10.23887/jippg.v3i2.29087
Haryani, R., Lubis, M. J., & Darwin. (2022). Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Pada Kinerja Guru. Basicedu, 6(3), 3373–3383.
Hiemstra, R., & Brockett, R. G. (2012). Reframing the Meaning of Self-Directed Learning: An Updated Modeltt. Adult Education Research Conference Proceedings, 155–161.
Honey, M., & Marshall, D. (2003). The impact of on-line muti-choice questions on undergraduate student nurses’ learning. Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference of the Australasian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education (ASCILITE), 236–243.
Indajang, K., Jufrizen, J., & Juliandi, A. (2020). Pengaruh Budaya Organisasi dan Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kompetensi Dan Kinerja Guru Pada Yayasan Perguruan Sultan Agung Pematangsiantar. Jupiis: Jurnal Pendidikan Ilmu-Ilmu Sosial, 12(2), 393. https://doi.org/10.24114/jupiis.v12i2.17881
Ismayilova, K., & M.Klassen, R. (2019). Research and teaching self-efficacy of university faculty: Relations with job satisfaction. International Journal of Educational Research, 98, 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2019.08.012
Jaliah, Fitria, H., & Martha, A. (2020). Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Manajemen Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru. Journal of Education Research, 1(2), 146–153.
Jaya, W. S. (2021). Kinerja Guru Ditinjau dari Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Motivasi Kerja. Jurnal Obsesi : Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini, 6(3), 1286–1294. https://doi.org/10.31004/obsesi.v6i3.1738
Kartini, K., Ahmad, S., & Eddy, S. (2020). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Komunikasi Interpersonal Terhadap Kinerja Guru. Journal of Education Research, 1(3), 290–294.
Kleij, F. M. van der. (2019). Comparison of teacher and student perceptions of formative assessment feedback practices and association with individual student characteristics. Teaching and Teacher Education, 85(1), 175–189.
Krueger, R. A., & Casey, M. A. (2015). Focus groups: A practical guide for applied research. Sage Publications, Inc.
Latinapa, M. M., Arsyad, A., & Suking, A. (2021). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah, Kemampuan Komunikasi Interpersonal Guru, dan Komitmen Kerja Guru Terhadap Pengendalian Konflik Di SD N Kecamatan Ratolindo Kabupaten Tojo Una-Una. Jurnal Normalita, 9(3), 386–401.
Mahvelati, E. H. (2021). Learners’ perceptions and performance under peer versus teacher corrective feedback conditions. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2021.100995
Marce, S., Ahmad, S., & Eddy, S. (2020). Manajemen Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Sebagai Administrator Dalam Peningkatan Kompetensi Guru. DAWUH: Islamic Education Journal, 1(2), 76–81.
Mufti, F. N., Sutama, & Suyatmini. (2021). Penanganan Konflik Berbasis Islami di Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Basicedu, 5(6), 6236–6248.
Nasrudin, A. H., Unsa, F. F., Aini, F. N., Arifin, I., & Adha, M. A. (2019). Manajemen Konflik dan Cara Penanganan Konflik Dalam Organisasi Sekolah. Tadbir: Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan Islam, 9(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.2991/icet-19.2019.7
Nazayanti, Wahyudi, & Chiar, M. (2019). The Influence of Transformational Leadership and School Environment on Academic Achievement of PAUD Teachers at West Pontianak District. Journal of Education, Teaching and Learning (JETL), 4(1), 40–48.
Nugroho, S. (2020). Kontribusi Komunikasi dan Keterampilan Manajemen Konflik Kepala Sekolah terhadap Kinerja Guru. Jurnal Pembangunan Pendidikan: Fondasi Dan Aplikasi, 7(1), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.21831/jppfa.v7i1.24774
Putranti, H. R. D., & Harianti, E. (2022). Upaya Meningkatkan Kinerja Pegawai Melalui Kepemimpinan Transaksional dan Pengembangan Karir. Jurnal Ilmiah Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, 15(1), 145–154.
Rachmawati Aziizah, D. (2018). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Budaya Organisasi terhadap Kinerja Guru dengan Kepuasan Kerja. Industrial Engineering Journal, 7(2), 18–24.
Ratmini, N. A., Natajaya, I. N., & Sunu, I. G. K. A. (2019). Kontribusi Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah, Komitmen Organisasi , Iklim Kerja Dan Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Guru SMP N 2 Singaraja. Jurnal Administrasi Pendidikan Indonesia, 10(2), 91–100.
Rokhani, C. T. S. (2020). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Sekolah di SDN Dengkek 01 Pati. Journal Industrial Engineering & Management Research ( Jiemar), 1(2), 1–8.
Rosaliawati, B. N., Mustiningsih, M., & Arifin, I. (2020). Hubungan Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Dan Kinerja Guru. Jurnal Administrasi Dan Manajemen Pendidikan, 3(1), 61–71. https://doi.org/10.17977/um027v3i12020p61
Rosid, M. H. Al, & Mukarromah, M. (2020). Korelasi Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dengan Motivasi Guru. Jurnal Tarbiyatuna, 1(2), 105–112.
Solihin, E., Giatman, M., & Ernawati, E. (2021). Dampak Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah pada Kepuasan Pekerjaan Guru dan Motivasi Kerja. Jurnal Imiah Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran, 5(2), 279. https://doi.org/10.23887/jipp.v5i2.34420
Sukiyanto, & Maulidah, T. (2020). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Motivasi Guru dan Karyawan. Jurnal Pendidikan Edutama, 7(1), 127–141.
Sulfemi, W. B. (2020). Pengaruh Rasa Percaya Diri Dan Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru. Nidhomul Haq : Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan Islam, 5(2), 157–179. https://doi.org/10.31538/ndh.v5i2.557
Sutrisno, E. (2014). Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia (6th ed.). Prenada Media Group.
Syarifah, L. S. (2019). Implementasi Pendidikan Karakter : Sebuah Kajian Ilmiah dari Perspektif Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah. Nizamul ‘Ilmi: Jurnal Manajemen Pendidikan Islam (JMPI), 04(1), 1–21.
Taufik, M. (2019). Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Transformasional Kepala Sekolah Terhadap Kinerja Guru. Wahana, 3(2), 465–478. https://doi.org/10.17509/jpm.v4i2.18012
Wisda, R. S. (2021). Persepsi Guru Tentang Kepemimpinan Sekolah dasar Negeri. Jurnal Administrasi Dan Manajemen Pendidikan (JAMP), 4(4), 358–363.
Wote, A. Y. V., & Patalatu, J. S. (2019). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Transformasional dan Kepuasan Kerja terhadap Kinerja Guru Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Ilmiah Sekolah Dasar, 3(4), 455–461.
Yanti, G. (2022). Persepsi Pegawai Terhadap Gaya Kepemimpinan Atasan di Dinas Pendidikan Kota Padang Panjang. Ilmu Hukum Humaniora Dan Politik, 3(1), 8–14.
Yeni, F., & Nellitawati. (2018). Persepsi Guru tentang Kepemimpinan Transformasional Kepala Sekolah. Jurnal Bahana Manajemen Pendidikan, 7(1), 51–59.
Zed, M. (2008). Metodologi Penelitian Kepustakaan. Yayasan Obor, Jakarta.
Zuldesiah, Z., Gistituati, N., & Sabandi, A. (2021). Kontribusi Gaya Kepemimpinan dan Pelaksanaan Supervisi Kepala Sekolah terhadap Kinerja Guru-guru Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Basicedu, 5(2), 663–671. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v5i2.791
Zulfan, Z., Musifuddin, M., & Murcahyanto, H. (2021). Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah sebagai Sistem Kontrol dan Pengaruhnya terhadap Kinerja Operator Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Basicedu, 5(6), 6005–6010. https://doi.org/10.31004/basicedu.v5i6.1693
Zulfiter, Fitria, H., & Nurkhalis. (2020). Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan Kepala Sekolah dan Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Guru. ISEJ: Indonesian Science Education Journal, 1(3), 269–277.