Research Article - (2025) Volume 20, Issue 4
Organizational Commitment Digital Literacy Professional Teachers And The Role Of Principal Digital Leadership In Buildin
Hasanudin Hasanudin*, Sowiyah Sowiyah, Riswanti Rini, Bujang Rahman and Handoko Handoko*Correspondence: Hasanudin Hasanudin, Doctoral Program in Education, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, University of Lampung, Indonesia, Email:
Received: 25-May-2025 Published: 02-Jul-2025 , DOI: doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15796074
Abstract
This study aims to analyze and determine the influence of organizational commitment, digital literacy, teacher professionalism, and the role of digital leadership of the principal in building an innovative organizational culture in educational units. By understanding the interaction between these factors, it is hoped that effective strategies can be identified to increase innovation in the educational environment.
The study used a quantitative approach with an explanatory research design. Data were collected through questionnaires distributed to junior high school principals throughout Lampung Province. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive and inferential statistical techniques to identify patterns of relationships between research variables and measure the influence of each factor on innovative organizational culture.
The results of the study indicate that (1) organizational commitment does not have a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership, which can be interpreted as meaning that organizational commitment does not contribute much to the principal's digital leadership; (2) literacy has a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership; (3) teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership. (4) Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture; (5) Digital literacy does not have a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture, which can be interpreted as meaning that digital literacy does not contribute much to organizational culture but contributes positively to the principal's digital leadership; (6) Teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on organizational culture; (7) Principal digital leadership has a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture; (8) Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership. The principal's digital leadership variable is simultaneously influenced by the variables of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism. (9) Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on the variable of innovative organizational culture. The results of quantitative analysis show that innovative organizational culture is simultaneously influenced by organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism.
Keywords
Organizational commitment, digital literacy, principal digital leadership, innovative organizational culture
Introduction
The 21st century is often referred to as the Industrial Revolution 4.0 or Digital Era, which is marked by drastic changes in the way people live, work, and interact with each other due to technological breakthroughs. Currently, all aspects of human life have been greatly influenced by the new digital environment supported by information and communication technology (Limna et al., 2022). Expanding access to innovative technologies such as automated machines, robotic devices, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital networks continues to trigger digital transformation in modern society (Azrai et al., 2020; Oberer & Erkollar, 2018). Even the acceleration of the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the world of education and learning during the pandemic became one of the issues emphasized and discussed in the G20 forum in 2022, namely Universal Quality Education, Digital Technologies in Education, Solidarity and Partnership, and The Future of Work Post Covid-19.
This digital transformation demands reform in the organizational culture of educational units. The organizational culture of schools in the era of digital transformation should support innovation, collaboration, and the use of technology to improve learning. It is important to have an open attitude towards change, facilitate technology training, and ensure digital security in the educational environment. Zhao (2016) stated that a school organizational culture that supports innovation and collaboration, and uses technology wisely, is the key to improving the effectiveness of learning in the era of digital transformation. The organizational culture of schools in the era of digital transformation should be supported by progressive digital leadership. Principals need to promote an open attitude towards innovation, motivate staff to develop digital skills, and strategically integrate technology into learning. Effective digital leadership encourages collaboration, rapid adaptation to change, and ensures the use of technology to improve efficiency and learning outcomes.
A successful school organizational culture in the era of digital transformation requires progressive digital leadership, encouraging innovation, collaboration, and strategic use of technology to enhance learning (Sheninger, 2014). The influence of technology in education in the era of growing globalization is very significant and unavoidable (Hartati et al., 2023). In general, digital technology increases accountability, efficiency, and transparency in administration, helps reduce expenses, and produces better governance (Tulungen et al., 2022). Implementing digital transformation is a primary goal in digital leadership. Businesses and organizations have the ability to transform their culture and work environment by implementing this leadership approach (Wujarso et al., 2023).
Leadership plays a central role in adopting the use of technology in the era of industry 4.0. Leaders need to have strong digital skills and emotional agility in operating in uncertain and complex environments. In the process of decision-making and innovation, effective leaders operate in a rapid learning cycle (Mihai & Creţu, 2019). A digital leader is someone who has a vision, is able to motivate change, combine business ideas for projects, and build relationships through creating new opportunities for partnerships, joint ventures, outsourcing, and other forms of collaboration (Fisk, 2002). Digital leadership is used as an umbrella term to refer to all types of these leadership models that aim for the successful integration of digital technologies into organizational functions and improvements (Karakose et al., 2022). As an innovative, change-oriented, and team-based leadership model, digital leadership is not only about using ICT or digital technology in carrying out leadership functions in schools, but includes several important elements such as having certain leadership skills and qualities, providing professional development and support, forming a digital-friendly culture, developing positive relationships, enabling systemic and structural improvements (Hamzah et al., 2021; Yusof et al., 2019). Digital leaders not only adapt to rapidly changing technologies and innovations but also promote the effective integration of these technologies into the learning environment through modeling and professional support (Hamzah et al., 2021). According to a recent study by Karakose et al. (2022) digital leaders are proficient in using digital technology, providing support for digital transformation and technology-based professional development, forming a digital learning culture, and using leadership skills to optimize the benefits of digital technology for learning.
Meyer and Allen Meyer and Allen in Jeon (2020) and Marliza et al. (2022) divide organizational commitment into three main components, namely affective commitment, continuance commitment, and normative commitment. When associated with the leadership of the principal, in the context of this organizational commitment, the principal plays a key role in shaping and influencing the commitment of educational staff members, including teachers and administrative staff, in an educational institution. Affective commitment component, the principal builds positive interpersonal relationships, provides emotional support to staff, and promotes an inclusive school culture can encourage affective commitment from staff members. Principals who pay attention to individual needs, recognize their contributions, and create a pleasant work environment can increase staff pride and satisfaction, supporting affective commitment.
Digital literacy is a term that is generally understood to refer to the ability or competence related to the skilful use of computers and information technology (Leaning, 2019). Digital literacy is concluded as an individual's ability to obtain and evaluate information, use that information effectively, create new content using the information obtained, and share and communicate the new information using appropriate technology (Reddy et al., 2020). Digital literacy refers to the skills, knowledge, and understanding that individuals need to function effectively in a society that is increasingly dominated by digital technology. It involves the ability to use, understand, evaluate, and participate critically with various types of digital media and information technology. Digital literacy includes not only technical aspects, but also critical and ethical dimensions in using digital technology.
Teacher professionalism is defined as broad and deep knowledge of the subject matter (field of study) to be taught, as well as mastery of methodology in the sense of having theoretical conceptual knowledge, being able to choose the right method, and being able to use it in the teaching and learning process Bempah et al. (2023). Combining broad knowledge of the subject matter and mastery of methodology, teachers create an effective learning environment and support holistic student development. This teacher professionalism supports the realization of a quality learning process that is relevant to student needs. Sharma (2017) divides indicators regarding teacher professionalism, that professional teachers have networking skills, communication skills, thinking skills, nurturing skills, and management knowledge.
Method
The research design used is explanatory research, which aims to explain the relationship between two variables that are suspected of having a causal relationship. The type of research used is associative research, in this case explanatory research conducted by a researcher using the associative method. The associative method itself is a method for seeing the causal relationship (cause and effect) between the independent variable (the cause of the emergence of the dependent variable) and the dependent variable (becoming the effect of the independent variable). In this method, researchers will focus on studying the causal relationship that may occur in the two variables in the study. So, from the beginning the researcher focuses on finding the relationship and can get a scientific explanation.
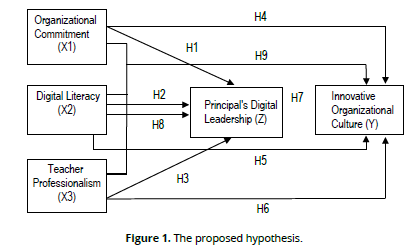
In this study, the researcher tested the relationship between variables, between organizational commitment, digital literacy, teacher professionalism, and the role of digital leadership of the principal on the formation of an innovative organizational culture in educational units. This approach was chosen because it is relevant to analyze the extent of the influence of each variable on an innovative organizational culture and to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between these variables. In general, the proposed hypothesis can be described in the following chart (Figure 1).
The research was conducted in a number of junior high schools in Lampung Province in the even semester of the 2023/2024 academic year from March to June 2024. The population used in this study were all junior high school principals in Lampung Province, totalling 1,475 people with a sample size of 315 principals.
The data collection process was carried out using a questionnaire method, where researchers compiled a number of written questions given to respondents. The results of this questionnaire were then processed using data processing software. The data analysis method used in this study is a descriptive statistical method, namely data analysis to obtain the distribution of respondent responses through the size of the mean, standard deviation and inferential statistics through Structural Equition Model analysis with Partial Least Square (SEM-PLS) to analyze the influence between variables.
Research Result
First Hypothesis Testing
The first hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Organizational commitment does not have a positive and significant effect on digital leadership.
Ha: Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on digital leadership.
The results showed that there was no positive and significant influence of Organizational Commitment on the Principal's Digital Leadership (Z) because the t-value <t table (1.505 <1.96) or P-values> 0.05 (0.132>0.05), so Ho was accepted and Ha was rejected. While the positive coefficient value means that there is no positive and significant influence of variable X1 on the Principal's Digital Leadership (Z). The strength of the relationship between organizational commitment and the Principal's Digital Leadership is 0.09. The results of this analysis also show that the determination coefficient is 0.0081, which means that the support and contribution of organizational commitment to the digital leadership of Junior High School principals throughout Lampung is 0.81%. This means that Ha which states that there is a positive and significant influence of organizational commitment on the digital leadership of Junior High School principals throughout Lampung is very small and has the consequence that Ha is rejected and Ho is accepted.
Second Hypothesis Testing
The second hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Digital literacy does not have a positive and significant effect on digital leadership.
Ha: Digital literacy has a positive and significant impact on digital leadership.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is an influence of Digital Literacy on the Principal's Digital Leadership because the calculated t value> t table (5.414> 1.96) or P-values <0.05 (0.00<0.05), so Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted, while the coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if Digital literacy increases, the Principal's Digital Leadership will increase. The strength of the relationship between digital literacy and the principal's digital leadership is 0.394. The results of this analysis also show that the coefficient of determination is 0.1552, which means that the support and contribution of digital literacy to the digital leadership of junior high school principals throughout Lampung is 15.52%. this means that Ha which states that there is an influence of digital literacy on the digital leadership of junior high school principals throughout Lampung is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. It can be concluded that the strength of the relationship between digital literacy and the digital leadership of junior high school principals throughout Lampung is 0.1552, which means that the relationship can be categorized as a very low relationship.
Third Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Teacher professionalism does not have a positive and significant influence on digital leadership.
Ha: Teacher professionalism has a positive and significant influence on digital leadership.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is a positive and significant influence of the Teacher Professional Variable on the Principal Leadership variable. This is because the t-value> t table (6.154> 1-96) or P-values <0.05 (0.00<0.05), so Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. The coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if teacher professionalism increases, the Principal Leadership will increase. The strength of the relationship between teacher professionalism and the principal's digital leadership is 0.482. The results of this analysis also show that the coefficient of determination is 0.2323, which means that the support and contribution of the teacher professional variable to the digital leadership of junior high school principals throughout Lampung is 23.23%. This shows that Ha, which states that there is a positive and significant influence of the teacher professional variable on the digital leadership of junior high school principals throughout Lampung, is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. Based on these findings, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between teacher professionalism and the principal's digital leadership is 0.2323, which means that the relationship is categorized as a low relationship. The contribution given by teacher professionalism to the principal's digital leadership is 23.23%.
Fourth Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Organizational commitment does not have a positive and significant effect on organizational culture.
Ha: Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on organizational culture.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is an influence between the variables of Organizational Commitment on Innovative Organizational Culture. This is because the calculated t value> t table (2.497> 1.96) or the P-values <0.05 (0.006<0.05), so Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. The coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if organizational commitment increases, innovative organizational culture will also increase. The strength of the relationship between organizational commitment and innovative organizational culture is 0.139. The results of this analysis also show that the coefficient of determination is 0.0193, which means that the support and contribution of organizational commitment is 1.93%. This means that Ha, which states that there is a positive and significant influence of organizational commitment on innovative organizational culture, is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. Based on this description, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between organizational commitment and innovative organizational culture is 0.139, which means that the relationship can be categorized as a low relationship. This means that the higher the level of organizational commitment, the higher the innovative organizational culture. The contribution of organizational commitment to innovative organizational culture is 1.93%.
Fifth Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Digital Literacy does not have a positive and significant effect on organizational culture.
Ha: Digital Literacy has a positive and significant impact on organizational culture.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is no significant influence between digital literacy variables on innovative organizational culture. This is because the t-value <t table (1.472 <1.96), or the P-value> 0.05 (0.071> 0.05). so that Ho is accepted and Ha is rejected. While the coefficient value is positive. The strength of the relationship between digital literacy and organizational culture is 0.153. These results also show that the coefficient of determination is 0.0234, which means that the support and contribution of digital literacy to innovative organizational culture is 2.34%. This means that Ha, which states that there is a positive and significant influence of digital literacy on the organizational culture of junior high school principals in Lampung, is very small and has the consequence that Ha is rejected and Ho is accepted. Based on the description here, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between digital literacy and innovative organizational culture is 0.153, which means that the relationship can be categorized as a weak relationship. This means that the higher the level of digital literacy, the higher the innovative organizational culture. The contribution of digital literacy to innovative organizational culture is 2.34%.
Sixth Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Teacher professionalism does not have a positive and significant influence on organizational culture.
Ha: Teacher professionalism has a positive and significant influence on organizational culture.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is a significant influence between the teacher professional variable and the innovative organizational culture. This is evidenced by the calculated t value> t table (2.261> 1.96) or the P-value <0.05 (0.011<0.05), so Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. The coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if the teacher professional increases, the organizational culture will increase. The strength of the relationship between teacher professionalism and organizational culture is 0.184. These results also show that the determination coefficient is 0.0338, which means that the support and contribution of teacher professionalism to organizational culture is 3.38%. This means that Ha, which states that there is a positive and significant influence of the teacher professional variable on the innovative organizational culture variable, is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. Based on this description, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between teacher professionalism and innovative organizational culture is 0.184, which means that the relationship can be categorized as a low relationship. This means that the higher the professionalism of teachers, the higher the innovative organizational culture tends to be. The contribution given is 3.38%.
Seventh Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Digital leadership does not have a positive and significant effect on organizational culture.
Ha: Digital leadership has a positive and significant impact on organizational culture.
Based on the Path Coefficients and T-Statistics tables, there is an influence of the principal's digital leadership (Z) on innovative organizational culture (Y). This is because t count> t table (6> 1.96) or P values <0.05 (0.006<0.05), so Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. While the coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if the Principal's Digital Leadership increases, the innovative organizational culture increases. The strength of the relationship between the principal's digital leadership and innovative organizational culture is 0.502. These results indicate that the determination coefficient is 0.2520, which means that the support and contribution of the principal's digital leadership to innovative organizational culture is 25.20%. This means that Ha, which states that there is a positive and significant influence of the principal's digital leadership variable on innovative organizational culture, is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. Based on this description, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between the principal's digital leadership and innovative organizational culture is 0.502, which means that the relationship can be categorized as moderate. This means that the higher the level of digital leadership of the principal, the higher the organizational culture tends to be. The contribution given by the principal's digital leadership to organizational culture is 25.20%.
Eighth Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism do not have a positive and significant effect on digital leadership.
Ha: Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant influence on digital leadership.
There is a significant and positive influence of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism on the principal's digital leadership. This is because the P-value is smaller than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05). So Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. While the coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism increase, the principal's digital leadership will increase. The strength of the relationship between the variables Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Digital Leadership is 0.935. These results show that the coefficient of determination is 0.875, which means that the support and contribution of Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Digital Leadership by 87.5%. This means that Ha which states that there is a positive and significant influence of the variables Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Digital Leadership is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected. Based on this description, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on digital leadership of 0.935, which means that the relationship can be categorized as high. This means that the higher the level of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism, the higher the digital leadership tends to be. The contribution made by the principal's digital leadership to organizational culture is 87.5%.
Testing the Ninth Hypothesis
The hypothesis proposed is:
Ho: Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism do not have a positive and significant effect on organizational culture.
Ha: Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant influence on organizational culture.
There is a significant and positive influence of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism on Innovative organizational culture. This is because the P-value is smaller than 0.05 (0.00 <0.05). So Ho is rejected and Ha is accepted. While the coefficient value is positive, meaning that the influence is positive, namely if organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism increase, Innovative Organizational Culture will increase. The strength of the relationship between the variables Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Digital Leadership is 0.927. These results show that the coefficient of determination is 0.859, which means that the support and contribution of Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Organizational Culture by 85.9%. This means that Ha which states that there is a positive and significant influence of the variables Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on Organizational Culture is accepted, with the consequence that Ho is rejected.
Based on this description, it can be said that the strength of the relationship between organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on digital leadership of 0.927, which means that the relationship can be categorized as high. This means that the higher the level of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism, the higher the organizational culture tends to be. The contribution made by the principal's digital leadership to organizational culture is 85.9%.
As for the results test hypothesis The table above is as follows (Table 1).
| Hypothesis | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P - Values | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Commitment (X1) -> Digital Leadership of the Head School (Z) | 0.061 | 1,481 | 0.069 | Not Significant |
| H2 | Literacy (X2) -> Digital Leadership Head School (Z) | 0.073 | 5.414 | 0 | Significant |
| H3 | Professional (X3) -> Head of Digital Leadership School (Z) | 0.078 | 6.19 | 0 | Significant |
| H4 | Commitment (X1) -> Culture Organization Innovative (Y) | 0.056 | 2,497 | 0.006 | Significant |
| H5 | Literacy (X2) -> Culture Organization Innovative (Y) | 0.104 | 1,472 | 0.071 | Not Significant |
| H6 | Professional (X3) -> Culture Organization Innovative (Y) | 0.081 | 2.276 | 0.011 | Significant |
| H7 | Head of Digital Leadership School (Z) -> Culture Organization Innovative (Y) | 0.084 | 6 | 0 | Significant |
| H8 | Commitment organization , digital literacy and teacher professionalism > digital leadership head school | 0.576 | 31,432 | 0 | Significant |
| H9 | Commitment organization , digital literacy and teacher professionalism > culture organization . | 0.576 | 32.173 | 0 | Significant |
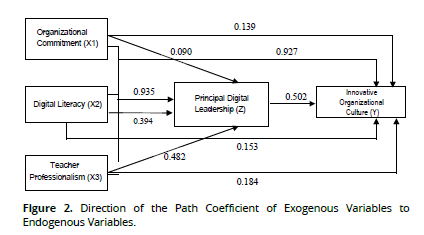
The path direction of the path coefficient above is as follows: (Figure 2).
In the image above looks magnitude contribution each and every variable Good variable simultaneous and also variable partial exogenous to endogenous variables. Contribution the to inform condition culture organization innovative can engineered with strengthen variable exogenous especially commitment organization, digital literacy and teacher professionalism. Variables exogenous the can mediated with digital leadership head school. Head digital leadership school have role important in effort realize culture organization innovative. Especially If in a way simultaneous variable exogenous can realized integrally, then the process for realize culture organization innovative will the faster and efficient. This is show how importance cooperation all parties and awareness together will importance culture an innovative organization applied in organization school.
Discussion
Based on the results of the calculation and hypothesis testing, it shows that two of the nine hypotheses are not partially and directly accepted but are simultaneously accepted and their influence is very strong. This shows that the research hypothesis has been tested for its truth, with the assumptions underlying the theory study supported by empirical research data in the field. The discussion in this section contains a discussion of the results of the hypothesis test consisting of nine hypotheses, the discussion is as follows:
The Influence of Organizational Commitment on Digital Leadership (Hypothesis 1)
Based on the results of data processing from the research conducted, it is known that there is no positive and significant influence of Organizational Commitment on the principal's digital leadership or in other words it can be considered that there is a very small influence and the consequence is that Ha is rejected and Ho is accepted.
In general, the description above shows that there is a positive relationship between the influence of organizational commitment on the digital leadership of the principal. However, its contribution is still very small. Therefore, the principal must understand the school environment better so that the principal is able to realize the organizational commitment together towards the school he leads.
The empirical findings of the previous organizational commitment variable found that the continuance commitment indicator as part of organizational commitment greatly helps coordination between sections with an average figure of 4.16. These data can be interpreted in the junior high school environment in Lampung as an object of organizational culture research in the form of synergy that has been carried out so far and has not been sufficient to help achieve organizational goals and has a very small influence on the Principal's Digital Leadership. So that the influence of organizational commitment does not have a significant effect on the principal's digital leadership. These findings are supported by previous data, namely research conducted by Prayuda (2022) that the principal's digital leadership is constructed by two dimensions, nine functions and behaviours practiced by the principal in the practice of digital leadership. The two dimensions are communication and school climate, while the nine functions include virtual meetings, virtual discussions, virtual information sharing, online file sharing, virtual communication, virtual teaching and learning supervision, virtual monitoring of student performance, virtual promotion of development and professionalism and virtual promotion of school goals. Based on these findings, it can be confirmed that organizational commitment does not affect the principal's digital leadership, but the principal's digital leadership is influenced by communication and school climate and nine other functions, namely virtual meetings, virtual discussions, virtual information sharing, online file sharing, virtual communication, teaching and learning supervision, virtual monitoring of student performance, virtual promotion of development and professionalism and virtual promotion of school goals.
Strengthening Prayuda's findings, the results of Rosita and Iskandar's (2022) research found several types of principal leadership styles that can be applied in the digital era, namely authoritarian, democratic, free, transformational, transactional, and authoritarian leadership styles. The conclusion that can be drawn from Rosita and Iskandar's (2022) research is that it can confirm that various challenges in the digital era must be faced by principals as leaders. The leadership style applied in schools is adjusted to the situation and conditions of the school. The leadership style used in the digital era is a leadership style that is able to provide a sense of comfort, but in general the more dominant is a democratic and transformational leadership style.
However, based on research by Rosita and Iskandar (2022), Jannah et al. (2023), Muslim (2021), and Gaol (2017), it can be indicated that organizational commitment can have a positive impact on the digital leadership of the principal. This can be seen in the affective commitment reflected in the leadership style of the principal, while this leadership style must be adjusted based on the situation and conditions of the school environment. The ability to identify the situation and conditions of the school is very much needed by the principal, so that the principal can determine the right style based on the school environment. So that the style he chooses can be used as a joint commitment to the school organization he leads.
The results of the study showing that there is no positive and significant influence between organizational commitment and the principal's digital leadership indicate several important aspects related to the dynamics of the school's organizational environment. First, this could indicate that other factors outside of organizational commitment are more dominant in influencing the principal's digital leadership. The rapidly changing and evolving organizational environment in the digital era may demand more specific skills and approaches, such as technological competence, adaptability, and innovative capabilities, which may not always be directly related to traditional organizational commitment.
The dynamic and complex organizational environment also demands leadership that is able to adapt quickly to technological changes. According to research by Apollo and Kahai (2003), digital leadership requires a different approach compared to conventional leadership, including the ability to manage teams virtually and utilize technology to achieve organizational goals. This means that high organizational commitment may not be enough to ensure effectiveness in digital leadership without the support of relevant technological skills and knowledge. In addition, organizational culture and work climate that encourage innovation and experimentation are also key factors that can influence digital leadership. According to research by Westerman, Bonnet, and McAfee (2014), success in digital transformation depends more on the organization's ability to create an environment that supports continuous learning and development, rather than just organizational commitment. Therefore, schools as organizations need to create a culture that encourages the use of technology and innovation in the teaching and learning process.
The results of this study indicate the importance of expanding the focus from organizational commitment to other factors that are more relevant to digital leadership. Schools need to ensure that they do not only rely on organizational commitment, but also facilitate the development of digital skills, create a culture of innovation, and adopt an adaptive and responsive leadership approach to technological change. The results of the study showed that there was no positive and significant influence between organizational commitment and the digital leadership of school principals could be influenced by the mind-set of the respondents. Mind-set, in this context, refers to the mind-set or mental attitude of school principals and members of the organization towards change and innovation, especially those related to digital transformation. Dweck (2006) put forward the concept of "fixed mind-set" and "growth mind-set," where individuals with a fixed mind-set tend to see abilities as something static, while those with a growth mind-set believe that abilities can be developed through effort and learning.
If respondents have a fixed mind-set, they may not see digital leadership as part of the organizational commitment that needs to be improved. They may feel that digital skills are not important or difficult to learn and apply in the context of leadership. In contrast, with a growth mind-set, respondents will be more open to developing their digital skills as part of the organization's commitment to achieving better educational goals. However, if respondents' mind-sets tend to be static, this can be a significant barrier to linking organizational commitment to effective digital leadership.
In addition, the insignificant influence of organizational commitment on digital leadership may also reflect a lack of perception of the urgency or relevance of digital transformation in the school environment. According to Fullan (2001), changes in education often require time and a deep understanding of the benefits of the innovation. If principals and organizational members do not see the immediate value or benefits of digital leadership, then their commitment to this aspect will be low, regardless of the overall level of organizational commitment.
The results of the study that showed no positive and significant influence between organizational commitment and the principal's digital leadership can also be linked to several concepts in psychology, especially organizational psychology and leadership. One important concept in organizational psychology is motivation theory, such as Herzberg's Two Factor Theory (1959). This theory distinguishes between hygiene factors that can prevent dissatisfaction, and motivator factors that can encourage satisfaction and high performance. If organizational commitment does not affect digital leadership, this indicates that organizational commitment is only a maintenance factor and not the main motivator factor in the context of digital leadership.
Digital leadership requires specific skills that involve adapting to new technologies, developing digital strategies, and the ability to lead teams through rapid digital change. Key motivating factors in digital leadership are more likely to be related to individual capabilities, such as digital intelligence, strategic vision, digital communication skills, and confidence in using technology. This suggests that while principals may be highly committed to their organization, this commitment is not enough to ensure they are effective digital leaders. They need to have or develop specific skills related to digitalization and technological transformation. Furthermore, Deci and Ryan’s (1985) theory of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation suggests that intrinsic motivation, which is the drive to do something because it is interesting or enjoyable, is more effective in the long run than extrinsic motivation, such as external rewards or pressures. In the context of digital leadership, intrinsic motivation related to curiosity about technology, a desire to innovate, and the satisfaction of overcoming digital challenges may play a greater role than more extrinsic organizational commitment.
Thus, while organizational commitment is important to maintain a stable framework, success in digital leadership requires stronger motivators and is more related to the individual's ability to adapt and innovate in a digital environment. Principals need to develop skills and attitudes that support digital leadership, beyond their commitment to the organization.
The Influence of Digital Literacy on the Principal's Digital Leadership (Hypothesis 2)
Based on the theory and results of this dissertation research, there is an influence of Digital Literacy on the Principal's Digital Leadership. Empirical findings in the previous quantitative analysis description showed that the average value of the digital literacy question indicator between sections was 4.16. This means that digital literacy in the form of information access and application of information is needed as a supporting system and has a positive effect on the principal's digital leadership. To develop the principal's digital leadership skills, the principal must be able to master digital literacy. The relationship between digital literacy and digital leadership is a mutually continuous relationship, namely if the principal's digital literacy increases, the principal's digital leadership will increase. This is supported by the findings in the question item that has the largest outer loading in question X2.12, namely the question in the literacy variable number twelve. The question is "in utilizing technology to increase the effectiveness of tasks and responsibilities, must have the ability to think creatively". The outer loading value is 0.891. This data informs that the increasing digital literacy will be reflected in question X2.12.
The results of this study are in line with those conducted by Jusnani, Isjoni, and Natuna (2021) that the results of the study obtained a significant influence between digital literacy and visionary leadership. Based on the results of this study, it can be concluded that the better the digital literacy of the principal, the better the digital leadership will be. The conclusion of this study shows a consistent relationship between digital literacy and the digital leadership of the principal. Meanwhile, the results of the study by Frandy et al (2023) stated that overall, digital literacy is an important key in the leadership of the principal in facing changes in new media in education. Literacy skills include aspects such as cultural, cognitive, constructive, communicative, self-confidence, creative, critical, and responsible. The results of testing the hypothesis of this dissertation are in line with the theory of action developed by Talcot Parson. Parsons' theory of action includes four systems, namely: cultural systems, social systems, personality systems, and organism systems (biological aspects of humans as a system). The system assumes the existence of unity between parts that are related to each other. The unity between the parts generally has a specific purpose. In other words, the parts form a unity (system) in order to achieve a certain goal or purpose (Abercromble et al., 1984:22). Meanwhile, the Behavioral system has an adaptation function, namely adjusting to the environment.
The conclusions obtained in previous studies support the results of hypothesis 2, namely the influence of digital literacy variables on the digital leadership of school principals, namely the better the digital literacy possessed by the principal, the better the digital leadership of the principal.
The Influence of Teacher Professionalism on Digital Leadership (Hypothesis 3)
From the data processing, it was found that there was a positive and significant influence of the Teacher Professional Variable on the Principal's Leadership variable.
Empirical findings of the data obtained from the quantitative analysis of this study indicate that the Teacher Professional indicator is in accordance with the competency in the teacher professional variable with an average value of 4.11 greater than the others, indicating that the teacher professional indicator owned by junior high schools throughout Lampung in this study is in accordance with the objectives of meeting standards. So that the teacher professional variable positively and significantly influences the principal's digital leadership variable. Research on the influence of teacher professionalism on the principal's digital leadership has not been conducted. So the results of this study are new findings. Previous data focused more on the influence of principal leadership on teacher professionalism. Teacher professionalism is a variable that has been used as a dependent variable in determining the direction of changes in the goals of the school organization. As the results of previous studies are as follows:
Ulfah et al's (2020) research found that principal leadership has a positive and significant impact on teacher professional competence. The results of the t-test of 80.714 are greater than the t-table of 1.97490, indicating a correlation between principal leadership and teacher professional competence of 0.976 in the very strong category. The magnitude of the influence of X1 on Y is 97.6%. The results of the study (Ulfah et al 2020) show that in order to improve teacher professionalism, it is necessary to improve and enhance principal leadership. In this study, principal leadership has a very strong and large contribution, namely 97.6%.
Evicasari's research (2021) shows that principal leadership has a significant effect on teacher professionalism by 37.4%. Organizational culture has a significant effect on teacher professionalism by 29.6%. Principal leadership has a significant effect on organizational culture by 17.2%. Based on these results, it can be concluded that principal leadership and organizational culture have a direct positive effect on teacher professionalism. Research by Ololah et al. (2022) that the contribution of principal leadership to teacher teaching performance is seen from the magnitude of the determination coefficient, which is 0.215, which means that the contribution of principal leadership to teacher teaching performance is 21.5% and the remaining 78.5 is influenced by other variables that were not studied. This influence is significant because the probability value is 0.015 <α 0.05.
Meanwhile, Purwoko's research (2018) shows that: (1) there is a positive and significant influence of principal leadership on teacher performance; (2) there is a positive and significant influence of teacher commitment on teacher performance; (3) there is a positive and significant influence of teacher discipline on teacher performance of; (4) there is a positive and significant influence of school culture on teacher performance; (5) there is a positive and significant influence of leadership performance, teacher commitment, teacher work discipline and school culture simultaneously on teacher performance. Research by Jaliah, Fitria, and Martha (2020) shows that (1) principal leadership has a positive and significant influence on teacher performance, (2) principal management has an influence on teacher performance, (3) work motivation and principal management have a positive and significant influence on teacher performance at SMP Negeri Prabumulih. Based on previous research, it can be concluded that the principal has an influence and contribution to teacher professionalism, this shows that in order to improve teacher professionalism, there needs to be improvement and positive changes in the principal's leadership.
However, in this dissertation research, the teacher professional variable is used as an independent variable and can have a positive and significant impact on the principal's digital leadership. This finding informs that there is a reciprocal relationship between teacher professionalism and the principal's digital leadership. Both variables, namely the teacher professional variable and the principal's digital leadership, can provide reciprocal contributions, so that both variables can simultaneously influence organizational culture. Therefore, educational institutions should position teachers as important variables in determining the direction of change in an educational institution. The efforts that can be made by educational institutions, especially private educational institutions, are to provide adequate welfare to teachers, involve teachers in determining the direction of organizational culture, position teachers on an equal footing with the principal's position in order to advance an innovative organizational culture, so that teachers have the same sense of responsibility as agents of change in organizational culture in education. These efforts are efforts to strengthen the position of professional teachers, so that teacher professionals can directly influence the principal's digital leadership.
The Influence of Organizational Commitment on Organizational Culture (Hypothesis 4)
Referring to the results of data processing, this study obtained information on the influence between the variables of Organizational Commitment on Innovative Organizational Culture. The empirical findings of this study, namely the influence of organizational commitment on organizational culture, are new findings, because no articles have been found that discuss the direct relationship between organizational commitment and organizational culture. The results of this study are the antithesis of Jazilah's (2023) research which concluded that organizational culture does not have a positive and significant impact on organizational commitment, but organizational culture influences organizational commitment through work motivation.
Meanwhile, the findings in this study state that the opposite relationship, namely organizational commitment can have a positive and significant influence on innovative organizational culture without going through mediation variables. As the results of the calculation of mediation variables are as follows (Table 2).
| Std Coefficient Value | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Commitment (X1) -> Principal's Digital Leadership (Z) -> Innovative Organizational Culture (Y) | 0.045 | 1,419 | 0.078 | No Mediating |
Source: data processed using the Smart PLS 3 application.
The table above shows that organizational commitment does not affect innovative organizational culture through the principal's digital leadership, but the organizational commitment variable directly affects the innovative organizational culture variable. This finding informs that the principal's leadership in mediating organizational commitment to innovative organizational culture at the junior high school level in Lampung has not shown its significance, but the organizational commitment possessed by each educator and education personnel has shown a positive and significant contribution to organizational culture. The findings of this study, especially the organizational commitment variable to organizational culture, strengthen previous findings, including:
The results of Jazilah's research (2023) stated that (1) organizational culture does not have a significant effect on organizational commitment; (2) organizational culture has a positive and significant effect on work motivation; (3) work motivation has a positive and significant effect on organizational commitment. Referring to the results of Jazilah's research, organizational culture does not contribute positively and significantly to organizational commitment, but the results of the author's dissertation research show the opposite relationship, that commitment is not influenced but commitment influences organizational culture. So that organizational commitment and organizational culture do not have a reciprocal relationship and only have a one-way relationship, namely organizational commitment influences organizational culture.
Meanwhile, several related researchers have been able to prove that organizational culture has a significant influence on organizational commitment. Ghina (2012) in her research explained that the term "commitment" which is important in all organizations is closely related to the sustainability aspect of organizations. This will determine their customer satisfaction with the quality of service. Therefore, in order to engage employee commitment, management must do several things to support these conditions, such as forming a culture that supports the creation of a comfortable work environment.
In contrast to the above research, the results of Wibawa and Putra's (2018) research show the opposite results, that organizational culture has a positive effect on organizational commitment, organizational culture has a positive effect on job satisfaction, job satisfaction has a positive effect on organizational commitment, and job satisfaction can mediate the influence of organizational culture on organizational commitment. Organizational commitment can be increased by maintaining employee job satisfaction, increasing collective commitment, and paying attention to employee salaries. Based on the description of the research above, it can be concluded that organizational commitment and organizational culture both have a reciprocal relationship, so that both contribute to each other.
The Influence of Digital Literacy on Organizational Culture (Hypothesis 5)
Referring to the results of research data processing, it was found that there was no influence between digital literacy variables on innovative organizational culture. However, the contribution of digital literacy can influence organizational culture through the digital leadership of the principal.
The empirical findings of this study show that to be able to realize organizational culture cannot only be done with digital literacy without the intervention of the principal. So that digital literacy does not have a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture. Here, the principal plays a very important role in creating organizational culture, so that digital literacy can influence organizational culture with the intervention of the principal's digital leadership.
As the results of measuring the mediation of literacy variables through the principal's digital leadership towards organizational culture are as follows (Table 3).
| Std Coefficient Value | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literacy (X2) -> Head of Digital Leadership School (Z) -> Culture Organization Innovative (Y) | 0.198 | 4.135 | 0 | Mediating |
Source: data processed using the Smart PLS 3 application.
| Std Coefficient Value | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teacher Professionalism (X3) -> Principal Digital Leadership (Z) -> Innovative Organizational Culture (Y) | 0.242 | 4.28 | 0 | Mediating |
Source: data processed using the SmartPLS 3 application.
The table above shows that digital literacy influences innovative organizational culture through the principal's digital leadership, but the digital literacy variable does not directly influence the innovative organizational culture variable. The findings of this study are in line with the results of previous studies. The previous studies are:
The results of the study by Dahman et al. (2023) showed that work motivation has a negative and significant effect on employee performance, then work ability has a positive and significant effect on employee performance and digital literacy has a positive and significant effect on employee performance. In this case, employee performance can be improved by increasing its competitiveness through increasing digital literacy. The results of the study by Muslimin and Idul (2020) stated that: (1) The attitudes and characters of students towards social restrictions due to the Covid-19 pandemic show a positive attitude, because they realize that this pandemic is dangerous for themselves and others. Generally, students try to avoid direct interaction with people. (2) Formation of attitudes and characters of students to avoid the Covid-19 outbreak through digital literacy. Research findings show that students use more digital applications to obtain useful information including carrying out online teaching and learning activities. Lecturers also always remind students during online lectures to protect themselves from the Covid-19 outbreak.
The findings of Muslimin and Idul's research (2020) show that students use digital applications more to obtain useful information including carrying out online teaching and learning activities. Lecturers also always remind students during online lectures to protect themselves from the Covid-19 outbreak. The World Economic Forum (2020) said that skills such as understanding technology, data analysis, and proficiency in using digital devices have become important in today's workplace. In facing the digital era, organizations are faced with new challenges and opportunities.
The paradigm shifts of HR management from administrative to strategic requires adaptive and innovative leadership. Digital skills development is the foundation for productivity and competitiveness. Therefore, employee training and development must be the main focus. A competency-based approach allows for more precise recognition of the skills needed. In addition, the use of technology and data analysis allows for more accurate and objective decision-making. Based on the findings and results of previous studies, it can be concluded that digital literacy plays an important role in shaping mind-sets so that they can ultimately be realized in organizational actions and culture.
The results of the study showing the absence of an influence of digital literacy on the innovative organizational culture of schools can be attributed to various environmental factors. One of the main factors is the infrastructure and access to technology available in schools. Although digital literacy may exist at the individual level, if the school environment does not support the use of technology, innovation in the organization is difficult to occur. Research by Zhang et al. (2020) shows that "adequate technological infrastructure is an important prerequisite for encouraging innovation in schools". In addition, administrative support and school policies also play an important role. An unsupportive environment or lack of policies that encourage the use of technology in learning can hinder the implementation of innovation even though individuals have good digital literacy. Research shows that "support from school management is critical to the successful implementation of educational technology" (Ertmer & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, 2010). Without this support, individual initiatives to implement innovation may not develop well.
Other environmental factors include the school culture itself. Schools with a culture that is resistant to change tend to have a harder time adapting to technological innovation. An environment that does not encourage collaboration and experimentation with new methods can also hinder the development of an innovative organizational culture. Fullan (2007) noted that “schools that are successful at innovation are those that have a collaborative culture and support experimentation and reflection.” The mind-set of respondents also played a significant role in the relationship between the lack of influence of digital literacy on the school’s innovative organizational culture. Respondents with a fixed mind-set may view technology as difficult or unchangeable, which can hinder the use of digital literacy to drive innovation. Dweck (2006) explained that individuals with a fixed mind-set often feel that their skills and abilities are limited and cannot be developed. This means that they may be less motivated to explore or implement new technologies, even if they have basic knowledge of the technology. In contrast, individuals with a growth mind-set tend to view challenges as opportunities to learn and grow. They are more open to new experiences and more likely to try innovative ways of using technology. Dweck (2006) argues that “individuals with a growth mind-set are more likely to take risks and engage in innovative processes because they believe that effort and learning can change outcomes”.
Respondents who have a positive attitude towards change tend to be more open to adopting new technologies and implementing them in their practices. This mind-set can influence how they adapt to digital literacy and contribute to an innovative organizational culture. Research by Kanter (2008) shows that “a positive attitude towards change is directly related to an individual’s readiness to adopt new technologies and innovate”. Respondents’ mind-set also influences their level of engagement and motivation in using technology for innovation. Respondents who feel confident in their ability to use technology effectively and who have intrinsic motivation to apply technology in the school context will be more successful in leveraging digital literacy to create cultural change. Compeau and Higgins (1995) highlight that “self-confidence in technological capabilities and intrinsic motivation play a significant role in determining the extent to which individuals engage in the use of technology for innovation”.
When connected to a psychological perspective, digital literacy may not have a direct effect on an innovative organizational culture if individuals in the organization experience anxiety or lack of confidence in using technology. Research by Compeau and Higgins (1995) shows that "individuals' confidence in using technology greatly influences the extent to which they will use the technology for innovation". If individuals are not confident or anxious about using technology, their digital literacy will not manifest in the form of innovation.
The Influence of Teacher Professionalism on Organizational Culture (Hypothesis 6)
From the results of data processing, it was found that there was a significant influence between the variables of teacher professionalism and innovative organizational culture. Empirical findings show that the strength of the relationship between teacher professionalism and organizational culture is 0.184. The contribution of teacher professionalism to innovative organizational culture in junior high schools throughout Lampung Province is still weak. The contribution of teacher professionalism can be strengthened by the existence of digital leadership of the principal, so that teacher professionalism can strengthen innovative organizational culture.
Edwards Deming stated that the use of good and proper management will lead organizations to improve their quality (they in this dissertation research are professional teachers). According to him, the key is continuous improvement and improving the quality of professional teachers will bring organizational culture to a better direction in the future. So that the findings of this study are in line with the theory developed by W. Edwards Deming. The relevant research related to the results of this dissertation research is: Research by Dewi and Khotimah (2020) The results of the study showed, 1) there is a significant influence between teacher professionalism on the quality of education, teacher professionalism has an influence of 78.5% on the quality of education and the remaining 21.5% is caused by other factors not observed by the author. 2) teacher work discipline on the quality of education has an influence of 83.5% and the remaining 16.5% is caused by other factors not observed by the author. 3) The results of the joint analysis between professionalism and teacher work discipline towards improving the quality of education are positive and have a very strong influence, this is indicated by the R value of 0.894 and the R square value of 0.799 or 79.9%.
Based on the research results of Dewi and Khotimah (2020), professionals have a positive and significant contribution to the quality of education, where the quality of education is part of the organizational culture that has been carried out by the organization. So that the research (Dewi and Khotimah 2020) strengthens the findings of this dissertation, that teacher professionals have a positive and significant contribution to innovative organizational culture. The better the teacher's professionalism, the better the innovative organizational culture. Because superior human resources are the main driving force of the quality of innovative organizational culture. Research by Darusman, Harapan, and Tahrun (2020) shows that: 1) there is a significant correlation between teacher performance and professional competence; 2) there is a significant correlation between school organizational culture and teacher performance at SD Gugus 10, Prabumulih City; and 3) there is a significant correlation between professional competence and organizational culture in schools. Darlima's (2017) research that teacher professionalism positively and significantly affects the performance of the t-value, with 5.027 greater than the t-table of 1.997, and principal leadership positively and significantly affects the performance of the t-value, with 3.468 greater than the t-table of 1.997, and organizational culture positively and significantly affects the performance of the t-value, with a value of 5.027 greater than the t-table of 1.997. The results are that teacher performance is significantly and positively influenced by teacher professionalism, principal leadership, and organizational culture. Teacher professionalism, principal leadership, and organizational culture as a whole affect teacher performance at SMP Negeri 14 Palembang City. Lian and Wardiah's (2022) research shows that: (1) Teacher Professionalism has a significant influence on teacher performance; (2) Teacher Professionalism and Principal Leadership have a significant influence on teacher performance; and (3) Teacher Professionalism and Principal Leadership have a significant influence on teacher performance. Therefore, significant values are not accepted.
Meanwhile, in this dissertation research, teacher professionalism influences innovative organizational culture through the digital leadership of the principal, as shown in the output of data processing using the following smart PLS 3 application:
Based on the table above, the principal's digital leadership has an important contribution in managing superior human resources to create an innovative organizational culture. Thus, the better the principal's digital leadership in mediating teacher professionalism, the better the innovative organizational culture will be. From several previous theories and studies, many explain the positive relationship between teacher professional variables and organizational culture.
The Influence of Principal's Digital Leadership on Organizational Culture (Hypothesis 7)
Referring to the results of the research data processing, it explains that there is an influence of the principal's digital leadership (Z) on the innovative organizational culture (Y). Empirical findings show a strong relationship between the principal's digital leadership and the innovative organizational culture in junior high schools throughout Lampung Province. Digital leadership has the greatest direct influence compared to other variables. This finding shows that the principal's digital leadership has an important role in realizing an innovative organizational culture. This seventh hypothesis strengthens the fifth hypothesis, that digital literacy does not affect the innovative organizational culture, but through digital leadership the principal can make a positive and significant contribution to the innovative organizational culture.
Likewise, the results of Evicasari's (2021) study showed that principal leadership has a significant effect on organizational culture by 17.2%. The findings of this study strengthen the findings of the author's dissertation that principal leadership has a very important role in realizing organizational culture. The principal's leadership position is a mediating independent variable against the dependent variable, so that with this mediation it will be easier to realize an innovative organizational culture. Research by Timan, Mustiningsih, and Imron (2022) shows that the five components of digital leadership, namely visionary leadership, digital age learning, excellent in professional, systemic improvement, and digital citizenship have a direct effect on teacher performance and student competence in the 21st century. The five components of digital leadership also have an indirect effect on student competence through teacher performance. The contribution of this study shows that with adequate digital leadership practices, supporting teachers' efforts to achieve the expected performance can improve student competence in the 21st century.
Research by Rantauwati, Zulkifli, and Putriana (2022) shows that the independent variable Digital Leadership Style (X1) affects the Employee Performance variable (Y) through the Intervening Variable Organizational Commitment (Z), the independent variable Career Development (X2) affects the Employee Performance variable (Y) through the Intervening Variable Organizational Commitment (Z), and the independent variable Organizational Culture (X3). Research by Saputra et al. (2022) shows that effective digital support and leadership have a positive, direct, and significant impact on job satisfaction and work engagement. To make office employees in private companies more satisfied and stressed during the digital transformation, companies must provide adequate organizational support and good digital leadership. Research by Jayanto et al (2023) shows that (1) leadership contribution has a positive and significant influence on job satisfaction, (2) leadership contribution does not have a positive and significant influence on employee performance, (3) organizational culture contribution has a positive and significant influence on job satisfaction, (4) organizational culture contribution has a positive and significant influence on employee performance, (5) job satisfaction has a positive and significant influence on employee performance, (6) leadership contribution has a positive and significant influence on employee performance mediated by job satisfaction, (7) organizational culture contribution has a positive and significant influence on employee performance mediated by job satisfaction.
From several previous theories and studies, the results support the results of this study which explain the influence of the positive relationship between the principal's digital leadership variable and innovative organizational culture at the junior high school level in Lampung Province.
The Influence of Organizational Commitment, Digital Literacy and Teacher Professionalism on Principal Digital Leadership (Hypothesis 8)
The results of data processing show that there is a significant and positive influence of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism on the digital leadership of school principals.
Empirical findings show a significant influence and relationship between organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism together or simultaneously on the principal's digital leadership. The simultaneous contribution is 87.5%, while the remaining 12.5% of the principal's digital leadership variable is influenced by other variables.
Siagian in Mulyasa (2003) that the direction to be taken by the organization towards its goals must be such that it optimizes the use of all available facilities and infrastructure. The direction in question is stated in the strategies and tactics that are formulated and implemented by the organization concerned. The formulator and determiner of the strategies and tactics are the leaders in the organization.
Furthermore, in the context of pedagogical competence, teaching requires knowledge according to Haberman in Hamalik, that one component of teacher knowledge that describes a good teacher is having pedagogy or teaching methodology, because in learning pedagogical competence must be owned and implemented by teachers to improve their work performance, plus supported by the theory of leadership effectiveness of the principal meeting the requirements, including: adhering to the goals achieved; enthusiastic; capable of providing guidance; fast and wise in making decisions; honest; intelligent; and capable in teaching and placing good trust and trying to achieve the goals, thus if all of the components in these variables can be improved and developed, it will be able to make teacher performance more optimal in junior high schools in Lampung.
The Influence of Organizational Commitment, Digital Literacy and Teacher Professionalism on Organizational Culture (Hypothesis 9)
There is a significant and positive influence of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism on Innovative organizational culture. Empirical findings show the influence and relationship between organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism together or simultaneously on organizational culture. This empirical finding is proof that organizational culture is influenced by the variables of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism by 85.9%, while the rest is influenced by variables outside the study by 14.1%.
The factors of organizational commitment and teacher professionalism are proven to influence organizational culture while digital literacy is not proven to partially influence organizational culture. However, the results of simultaneous tests of the three variables show that they can explain and predict organizational culture significantly.
After going through the stages of empirical data review of research related to organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism, it was concluded that organizational culture at the junior high school level in Lampung is a characteristic of an innovative organizational culture. An innovative organizational culture is definitively a combination of organizational commitment theory, digital literacy theory, and teacher professionalism theory. The combination of these theories is an intersection that connects the three.
Conclusion
The conclusions of the dissertation research results are as follows:
- Organizational commitment does not have a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership, it can be interpreted that organizational commitment does not contribute much to the principal's digital leadership. From the quantitative analysis with a contribution of (R = 0.09 or 0.81%), this value provides an illustration of the relationship that organizational commitment is not an indicator of the principal's digital leadership, so it is necessary to improve organizational commitment which has been part of the organizational culture in junior high schools throughout Lampung Province which is still neglected and as a form of coordination between sections to achieve planned goals and fulfil a quality innovative organizational culture.
- Literacy has a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership, namely if digital literacy increases, the principal's digital leadership also increases. The results of the quantitative analysis provide information that digital literacy contributes to digital leadership by (R = 0.394 or 15.52%). This value informs that 15.52% of digital leadership is influenced by digital literacy while 84.48% of digital leadership is influenced by other factors that exist in the school situation and conditions, such as teacher professionalism, work climate, teacher competence, facilities and infrastructure and should be in accordance with school conditions. This information shows that the information technology service facilities provided by Junior High Schools throughout Lampung Province are very important in supporting digital literacy, especially during the pandemic. The Secretariat as the unit responsible for information technology services should always monitor this service in order to facilitate access to information and complete work that supports the development of an innovative organizational culture.
- Teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership, namely if teacher professionalism increases, the principal's digital leadership also increases. The results of quantitative analysis show that the contribution of teacher professionalism to the principal's digital leadership is (R = 0.482 or 23.32%), this information shows that the teacher professionalism that has been owned by junior high schools throughout Lampung Province has been in accordance with school needs, this is intended to support the principal's digital leadership in realizing an innovative organizational culture.
- Organizational commitment has a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture, namely if organizational commitment increases, innovative organizational culture also increases. The results of quantitative analysis show that organizational commitment contributes to organizational culture by (R = 0.139 or 1.93%), this information shows that organizational commitment in junior high schools throughout Lampung Province has been implemented and has become part of the organizational culture, but its contribution is still very small. This potential will make it easier for school principals to realize an innovative organizational culture.
- Digital literacy does not have a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture, it can be interpreted that digital literacy does not contribute much to organizational culture but contributes positively to the digital leadership of the principal, which is (R = 0.153 or 0.23%). From the quantitative analysis, it provides a picture of the relationship that digital literacy is not an indicator of innovative organizational culture, so it is necessary to improve digital literacy which has been part of the organizational culture in junior high schools throughout Lampung Province which is still neglected and as a form of coordination between sections to achieve planned goals and fulfil a quality innovative organizational culture.
- Teacher professionalism has a positive and significant effect on organizational culture with a contribution of (R = 0.184 or 3.38%). This result provides information that if teacher professionalism increases, organizational culture will also increase. The relationship between superiors and subordinates is part of the organizational culture that will always support the development of teacher professionalism which will ultimately create an innovative organizational culture. This result shows that the teacher professionalism that has been possessed by junior high schools throughout Lampung Province has been in accordance with school needs, this is intended to support the digital leadership of the principal in realizing an innovative organizational culture.
- The principal's digital leadership has a positive and significant effect on innovative organizational culture with a contribution of (R = 0.0502 or 25.20%). The results of this quantitative analysis provide information that the higher the principal's digital leadership, the better the organizational culture. These results indicate that the digital leadership of junior high school principals in Lampung Province shows a direct influence and has a positive and significant impact on organizational culture. The principal's digital leadership is the core for realizing an innovative organizational culture. Meanwhile, the principal's digital leadership at junior high schools in Lampung Province has been able to realize an innovative organizational culture in their respective schools with a percentage of 25.20%.
- Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on the principal's digital leadership. These results indicate that the principal's digital leadership variable is simultaneously influenced by the variables of organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism. The simultaneous contribution is (R = 0.935 or 87.42%).
- Organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism have a positive and significant effect on the variable of innovative organizational culture. The results of quantitative analysis show that innovative organizational culture is simultaneously influenced by organizational commitment, digital literacy and teacher professionalism. This simultaneous influence has a large contribution, namely (R = 0.927 or 85.93%).
Bibliography
Avolio, B. J., & Kahai, S. S. (2003). Adding the "E" to E-Leadership: How it May Impact Your Leadership. Organizational Dynamics, 31(4), 325-338.
Azrai, M., Aqil, M., Suarni, Efendi, R., Z, B., & Arvan, RY 2020. Millet Cultivation Technology.
Bempah, HO, Abbas, N., & Djakaria, I. 2023. Comparison of Professional Competencies of Middle School Mathematics Teachers Based on Certification Status. Jambura Journal of Mathematics Education, 4(1), 98–109. https://doi.org/10.34312/jmathedu.v4i1.18219
Compeau, D. R., & Higgins, C. A. (1995). Computer self-efficacy: Development of a measure and initial test. MIS Quarterly, 19(2), 189-211.
Dahman, Yuliana, Goso Goso, Sahrir Sahrir, and Salju Salju. 2023. “The Role of Digital Literacy, Work Motivation, Work Ability in Improving the Performance of MSME Employees.” Jesya (Journal of Economics and Sharia Economics) 6 (2): 1784–93. Https://Doi.Org/10.36778/Jesya.V6i2.1191.
Darlima, Darlima. 2017. “The Influence of Teacher Professionalism, Principal Leadership and Organizational Culture on Teacher Performance at Smp Negeri 14 Palembang.” Jurnal Ecoment Global 2 (2): 63–72. Https://Doi.Org/10.35908/Jeg.V2i2.253.
Darusman, Darusman, Edi Harapan, and Tahrun Tahrun. 2020. “The Relationship Between Teacher Professional Competence and Organizational Culture with Teacher Performance at Elementary School Cluster 10, Prabumulih City.” Journal Of Education Research 1 (3): 188–92. Https://Doi.Org/10.37985/Joe.V1i3.20.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (1985). Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. New York: Plenum.
Dewi, R, and Khotimah, SH. 2020. “The Influence of Teacher Professionalism and Work Discipline on Improving the Quality of Education in Elementary Schools.” Elementary: Islamic Teacher Journal 8 (2): 279–94. Https://Doi.Org/10.21043/Elementary.V8i2.7839
Dweck, C.S. (2006). Mindset: The New Psychology of Success. New York: Random House.
Ertmer, P. A., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. T. (2010). Teacher technology change: How knowledge, confidence, beliefs, and culture intersect. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 42(3), 255-284
Evicasari, E. 2021a. “The Influence of Principal Leadership and Organizational Culture on Teacher Professionalism.” Journal of Educational Quality Circle 18 (1): 68–72. Https://Doi.Org/10.54124/Jlmp.V18i1.17.
———. 2021b. “The Influence of Principal Leadership and Organizational Culture on Teacher Professionalism.” Journal of Educational Quality Circle 18 (1): 68–72. Https://Doi.Org/10.54124/Jlmp.V18i1.17.
Fisk, P. 2002. The Making of a Digital Leader. Business Strategy Review, 13(1), 43–50.
Frandy et al. 2023. “The Urgency of Digital Literacy in Principal Leadership | Walean |Bahana Journal of Educational Management.” 2023. Https://Ejournal.Unp.Ac.Id/Index.Php/Bahana/Article/View/125274.
Fullan, M. (2001). Leading in a Culture of Change. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
__________ (2007). The New Meaning of Educational Change. Teachers College Press.
Gaol, NTL 2017. “Theory and Implementation of Principal Leadership Style.” Kelola: Journal of Educational Management 4 (2): 213–19. Https://Doi.Org/10.24246/J.Jk.2017.V4.I2.P213-219.
Ghina, Astri, 2012. The Influence of Corporate Culture on Organizational Commitment; case study of civil government organizations in Indonesia, International Journal of Basic and Applied Science Vol.1 No.2 2012.
Hamzah, HN, Khalid, M., & Wahab, JA (021. The effects of principals' digital leadership on teachers' digital teaching during the covid-19 pandemic in malaysia. Journal of Education and E-Learning Research, 8(2), 216–221. https://doi.org/10.20448/journal.509.2021.82.216.221
Hartati, S., Nurdin, D., & Arisandi, D. 2023. Digital Leadership Education in Learning at Abdurrab Vocational High School, Pekanbaru. Indonesian National Service Journal (JPN), 4(2), 238–244. https://doi.org/10.35870/jpni.v4i2.155
Herzberg, F., Mausner, B., & Snyderman, B. B. (1959). The Motivation to Work. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jaliah, Fitria, H., and Martha, A. 2020. “The Influence of Principal Leadership and Principal Management on Teacher Performance.” Journal Of Education Research 1 (2): 146–53. Https://Doi.Org/10.37985/Joe.V1i2.14.
Jannah, R., Rosyidin, AM, Nurmala, T., Yuningsih, N, and Yenny, E. 2023. “Leadership in the Digital Era and Its Implementation in Educational Institutions.” Jurnal Syntax Admiration 4 (2): 264–69. Https://Doi.Org/10.46799/Jsa.V4i2.557.
Jayanto, DHD (2023). Contribution of Leadership and Organizational Culture to Employee Performance in the Digital Era with Job Satisfaction as an Intervening Variable (Study at BPS Semarang Regency) (Doctoral dissertation, Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta).
Jazilah, K. 2023. “The Influence of Organizational Culture on Organizational Commitment Through Work Motivation.” Journal of Management Science, June, 445–57. Https://Doi.Org/10.26740/Jim.V11n2.P445-457.
Jeon, H. 2020. The Mechanism of Empathy and Relationship Commitment Through Emojis: Path to Perspective Taking, Inner Imitation, Emotional Empathy, and Relationship Commitment. SAGE Open, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020969675
Jusnani, H., Isjoni, and Natuna, DA 2021. “The Influence of Digital Literacy and Optimism on the Visionary Leadership of Junior High School Principals in Pekanbaru City.” Jumped Journal (Journal of Educational Management) 9 (2): 206. Https://Doi.Org/10.31258/Jmp.9.2.P.206-215.
Kanter, R. M. (2008). Change is the Only Constant: The New Rules of Change Management. Harvard Business Review Press.
Karakose, T., Polat, H., & Papadakis, S. 2022. Examining teachers' perspectives on school principals' digital leadership roles and technology capabilities during the covid-19 pandemic. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/su132313448
Leaning, M. 2019. An approach to digital literacy through the integration of media and information literacy. Media and Communication, 7(2 Critical Perspectives), 4–13. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v7i2.1931
Lian, B. and Wardiah, L. 2022. “The Influence of Teacher Professionalism and Principal Leadership on Teacher Performance at Sma Pgri 2 Palembang” 20.
Limna, P., Jakwatanatham, S., Siripipattanakul, S., & Kaewpuang, P. 2022. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education during the Digital Era Healthcare Strategies and Consumer Behavior View project Management View project. Advanced Knowledge. July. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361926050
Marliza, Y., Nyoto, & Sudarno. 2022. Leadership Style, Motivation, and Communication on Organizational Commitment and Employee Performance in the Rokan Hulu Regional General Hospital. Journal of Applied Business and Technology, 3(1), 40–55.
Mihai, R.-L., & Creţu, A. 2019. Leadership in the Digital Era. Valahian Journal of Economic Studies, 10(1), 65–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/vjes-2019-0006
Mulyasa, E. (2003). School-Based Management: Concept, Strategy, and Implementation. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Muslim, M. 2021. “Digital Leadership Vision of Elementary School Principals in the Era of Digital Technology.” Elementeris : Scientific Journal of Islamic Elementary Education 3 (1): 1–13. Https://Doi.Org/10.33474/Elementeris.V3i1.8796.
Muslimin, M and Idul, R. 2020. “The Influence of Digital Literacy Culture on the Formation of Community Attitudes and Characters in Social Restrictions Due to the Covid-19 Pandemic.” Journal of Language, Literature, and Culture 10 (3): 21–36. Https://Doi.Org/10.37905/Jbsb.V10i3.10540.
Oberer, B., & Erkollar, A. 2018. Leadership 4.0: Digital Leaders in the Age of Industry 4.0. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 7(4), 404–412. https://doi.org/10.33844/ijol.2018.60332
Ololah, Yasinta, Y., Pauweni, N., Hamdata, R., and Pasi, F. 2022. “The Influence of Principal Leadership on Teacher Teaching Performance in Elementary Schools.” Jurnal Bahana Manajemen Pendidikan 11 (2): 196–201. https://Doi.Org/10.24036/Jbmp.V11i2.121261.
Prayuda, RZ. 2022. “Digital Leadership of School Principals in the Digital Era : A Mini Review Article. ” International Journal Of Social, Policy And Law 3 (1): 13 – 18. https://Doi.Org/10.8888/Ijospl.V3i1.94.
Purba, R., Herman, H., Saputra, N., Shaumiwaty, & Fatmawati, E. F. (2024). Identifying the Implementation of Teaching English to Early Childhood in the Development of Language Acquisition. Pegem Journal of Education and Instruction, 14(2), 126–130. https://doi.org/10.47750/pegegog.14.02.15
Purwoko, S. 2018. “The Influence of Principal Leadership, Teacher Commitment, Teacher Work Discipline, and School Culture on Vocational High School Teacher Performance.” Journal of Educational Management Accountability 6 (2): 150–62. Https://Doi.Org/10.21831/Amp.V6i2.8467.
Rantauwati, EA, Zulkifli, and Putriana, L. 2022. “The Influence of Digital Leadership Style, Career Development and Organizational Culture on Employee Performance Through Organizational Commitment: The Influence Of Digital Leadership Style, Career Development And Organizational Culture On Employee Performance Through Organizational Commitment." Journal of Management and Accounting Research 2 (2): 38–49. Https://Doi.Org/10.55606/Jurima.V2i2.252.
Reddy, P., Sharma, B., & Chaudhary, K. 2020. Digital literacy: A review of literature. International Journal of Technoethics, 11(2), 65–94. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJT.20200701.oa1
Rosita, R., and Iskandar, S. 2022. “Principal Leadership Style in the Digital Era.” Basicedu Journal 6 (4): 6005–11. Https://Doi.Org/10.31004/Basicedu.V6i4.3127.
Saputra, Nopriadi, Putri, A, Danaswati, S., and Putri, S. 2022. “Testing the Influence of Digital Leadership and Perceived Organizational Support on Job Satisfaction and Work Engagement.” Journal Of Business & Applied Management 15 (2): 113. Https://Doi.Org/10.30813/Jbam.V15i2.3658.
Sharma. 2017. Teachers in a Digital Era. Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 17(G3), 11–14. Retrieved from https://computerresearch.org/index.php/computer/article/view/1633
Sheninger, E.C. (2014). Digital Leadership: Changing Paradigms for Changing Times. Jossey-Bass.
Timan, A., Mustiningsih, and Imron, A. 2022. “Digital Leadership of School Principals and Its Relationship with Teacher Performance and Student Competence in the 21st Century Era.” Jamp : Journal of Educational Administration and Management 5 (4): 323 – 33. Https://Doi.Org/10.17977/Um027v5i42022p323.
Tulungen, EEW, Saerang, DPE, & Maramis, JB 2022. Digital Transformation: The Role of Digital Leadership. EMBA Journal: Journal of Economics, Management, Business and Accounting Research, 10(2), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.35794/emba.v10i2.41399
Ulfah Et Al. 2020. “The Influence of Principal Leadership and Work Motivation on the Professional Competence of Public Elementary School Teachers | Journal of Learning Innovation in Schools.” 2020. Https://Ejournal.Pgrikotasemarang.Org/Index.Php/Jips/Article/View/166.
Wibawa, IWS, and Putra, MS 2018. “The Influence of Organizational Culture on Organizational Commitment Mediated by Job Satisfaction (Study at PT. Bening Badung-Bali)” 7 (6).
Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. (2014). Leading Digital: Turning Technology into Business Transformation. Harvard Business Review Press.
Wujarso, R., Seno Pitoyo, B., & Prakoso, R. 2023. The Role of Digital Leadership in the Digital Era. Journal of Information System, Applied, Management, Accounting and Research, 7(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.52362/jisamar.v7i1.720
Yusof, MR, Yaakob, MFM, & Ibrahim, MY 2019. Digital leadership among school leaders in Malaysia. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering, 8(9), 1481–1485. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.i8221.078919
Zhang, X., Wang, C., & Tang, Y. (2020). The impact of ICT infrastructure on innovation in education. Journal of Educational Technology Development and Exchange, 13(2), 105-120.