Full Length Research Article - (2023) Volume 18, Issue 2
The Effect Of Using Virtual Reality Technology Vr Box Glasses On Learning The Skill Of Shooting In Handball
Maen Ahmad Mahmoud Shalan**Correspondence: Maen Ahmad Mahmoud Shalan, Physical Education Department, Faculty of Sport Science, Mutah University, Jordan, Email:
Received: 08-Mar-2023 Accepted: 22-Mar-2023 Published: 22-Mar-2023
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to identify the effect of using Virtual Reality Technology, VR BOX, to learn the shooting skill of Handball for students of the College of Sport Sciences at Mutah University.
Methodology: The study used the experimental approach with a two-way design using an experimental and a control group, by comparing the pre and post measurement for each group and then comparing the two groups. The study population consisted of (54) students enrolled in the Handball course (1) in the College of Science Sports, Mutah University for the summer semester 2020/2021. Moreover, the study sample consisted of (30) students who were randomly chosen, and the study sample was divided into two groups, with (15) students for the experimental group learning the shooting skill using Virtual Reality Technology, VR BOX, for (6) weeks, with two meetings per week, and (15) for the control group, learning the shooting skill using the traditional method, for (6) weeks, with two meetings per week. The accuracy test was used to collect the study data.
Results: The study concluded that the use of learning with Virtual Reality, using VR BOX, contributed positively to learning the shooting skill of Handball, and the use of the traditional method contributed positively to learning the shooting skill of Handball, and the members of the experimental group that used Virtual Reality, using VR BOX as an educational method for the control group members who used the traditional method in learning the shooting skill of Handball.
Conclusion: The study recommended using VR BOX (Virtual Reality Box) as one of the modern teaching methods and tools to learn the shooting skill of Handball, holding educational courses for PE teachers (physical education teachers) to teach them how to use Virtual Reality, using VR BOX in teaching, and providing VR BOX as an educational tool in physical education colleges.
Keywords
Virtual Reality. VR BOX. Learning. Shooting skill.
EL EFECTO DEL USO DE LA TECNOLOGÍA DE REALIDAD VIRTUAL, GAFAS VR BOX, EN EL APRENDIZAJE DE LA HABILIDAD DE TIRO EN BALONMANO
ABSTRACTO
Objetivos: este estudio tuvo como objetivo identificar el efecto del uso de la tecnología de realidad virtual, VR BOX, para aprender la habilidad de tiro de balonmano para estudiantes de la Facultad de Ciencias del Deporte de la Universidad de Mutah.
Metodología: El estudio utilizó el enfoque experimental con un diseño de dos vías utilizando un grupo experimental y uno de control, comparando la medición previa y posterior para cada grupo y luego comparando los dos grupos. La población de estudio consistió en (54) estudiantes inscritos en el curso de balonmano (1) en la Facultad de Ciencias del Deporte de la Universidad de Mutah para el semestre de verano 2020/2021. Además, la muestra de estudio consistió en (30) estudiantes que fueron elegidos al azar, y la muestra de estudio se dividió en dos grupos, con (15) estudiantes para el grupo experimental aprendiendo la habilidad de disparar utilizando la tecnología de realidad virtual, VR BOX, para (6) semanas, con dos encuentros por semana, y (15) para el grupo control, aprendiendo la destreza del tiro por el método tradicional, durante (6) semanas, con dos encuentros por semana. La prueba de precisión se utilizó para recopilar los datos del estudio.
Resultados: El estudio concluyó que el uso del aprendizaje con Realidad Virtual, utilizando VR BOX, contribuyó positivamente al aprendizaje de la habilidad de tiro de Handball, y el uso del método tradicional contribuyó positivamente al aprendizaje de la habilidad de tiro de Handball, y los integrantes de la grupo experimental que utilizó Realidad Virtual, utilizando VR BOX como método educativo para los integrantes del grupo de control que utilizaron el método tradicional en el aprendizaje de la habilidad de tiro de Balonmano.
Conclusión: El estudio recomendó el uso de VR BOX (Caja de realidad virtual) como uno de los métodos y herramientas de enseñanza modernos para aprender la habilidad de tiro de balonmano, realizando cursos educativos para profesores de educación física (profesores de educación física) para enseñarles cómo usar la realidad virtual, usando VR BOX en la enseñanza y proporcionando VR BOX como una herramienta educativa en las universidades de educación física.
Palabras clave: Realidad Virtual. VR BOX. Aprendizaje. Habilidad de tiro.
O EFEITO DO USO DA TECNOLOGIA DE REALIDADE VIRTUAL, ÓCULOS VR BOX, NO APRENDIZADO DA HABILIDADE DE ARREMESSO NO HANDEBOL
ABSTRATO
Objetivos: Este estudo teve como objetivo identificar o efeito do uso da Tecnologia de Realidade Virtual, VR BOX, para aprender a habilidade de arremesso de Handebol para alunos da Faculdade de Ciências do Esporte da Mutah University.
Metodologia: O estudo utilizou a abordagem experimental com um design de duas vias usando um grupo experimental e um grupo de controle, comparando a medição pré e pós para cada grupo e, em seguida, comparando os dois grupos. A população do estudo consistiu em (54) alunos matriculados no curso de Handebol (1) no College of Science Sports, Mutah University para o semestre de verão 2020/2021. Além disso, a amostra do estudo consistiu de (30) alunos que foram escolhidos aleatoriamente e a amostra do estudo foi dividida em dois grupos, com (15) alunos do grupo experimental aprendendo a habilidade de tiro usando a Tecnologia de Realidade Virtual, VR BOX, para (6 ) semanas, com dois encontros semanais, e (15) para o grupo controle, aprendendo a habilidade de arremesso pelo método tradicional, por (6) semanas, com dois encontros semanais. O teste de precisão foi usado para coletar os dados do estudo.
Resultados: O estudo concluiu que o uso do aprendizado com Realidade Virtual, utilizando o VR BOX, contribuiu positivamente para o aprendizado da habilidade de arremesso do Handebol, e o uso do método tradicional contribuiu positivamente para o aprendizado da habilidade de arremesso do Handebol, sendo que os integrantes do grupo experimental que utilizou a Realidade Virtual, utilizando o VR BOX como método educacional para os integrantes do grupo controle que utilizaram o método tradicional no aprendizado da habilidade de arremesso do Handebol.
Conclusão: O estudo recomendou o uso do VR BOX (Virtual Reality Box) como um dos métodos e ferramentas modernas de ensino para aprender a habilidade de arremesso do Handebol, realizando cursos educacionais para professores de educação física (professores de educação física) para ensinálos a usar a Realidade Virtual, usando o VR BOX no ensino e fornecendo o VR BOX como uma ferramenta educacional nas faculdades de educação física.
Palavras-chave: Realidade virtual. VR BOX. Aprendizado. Habilidade de tiro.
Study Introduction
Recently, the world has witnessed rapid and remarkable progress in the development of knowledge, science and technology, which prompted many societies to include many of them in their political and economic plans as well as the educational system in order to keep pace with this knowledge and technological progress. The rapid progress in information technologies and modern communications in their various forms and their effectiveness within the educational process have led to the emergence of many scientific terms such as distance learning, e-learning and Virtual Reality. Paying attention to the quality of education is one of the indicators of the progress of any country, which directed many educators to use these educational technological innovations and make them the focus of their attention to be used in the educational process.
Virtual Reality Technology is one of the modern digital technological innovations that provides its users with creating a virtual environment that is free of boredom and increases their comprehension and concentration and saturates their inclinations and directions by creating an environment that resembles reality by showing fixed and moving objects as if they are in their real world in terms of embodiment and movement, and this is what we need to enrich the educational process and achieve its objectives are reflected in its programs and activities in a way that allows learners to adapt to the nature of the age and its technological innovations (Plancher et al., 2008).
Makransky and Petersrn (2021) indicated that the great abundance of modern technologies such as Virtual Reality Technologies and the increase in free progress software allowed anyone to build an attractive virtual experience that could be personal, public, or for specific purposes. Therefore, Virtual Reality Technologies are no longer simple technologies that can be neglected. However, they have become technologies of global feasibility that contribute to increasing interaction with the academic content or with peers in the educational process in an advanced and distinct way.
Virtual Reality is an advanced multimedia system that includes specific technical software that helps with sensory immersion, in addition to the possibility of considering it as a means of representing advanced content capable of simulating or imitating the real and imagined world (Mikropoulos and Natsis, 2011).
Virtual Reality can be achieved through several methods and tools. It consists of either pictorial representation of three-dimensional shapes, or representation of tools and services to be trained on, or representation of the environment or the place to be examined or toured within. The use of Virtual Reality aims to acquire the ability to accurately predict a specific behavior or a specific system in order to prove its effectiveness.
Virtual reality is a graphic simulation of real reality at the time when the user interacts with the system using special tools such as protective helmets, stereo headsets, gloves, glasses. The user shall have the ability to interact and control the direction of movement (Ahmed, 2021).
Allawi and Qutub (2022) confirm that virtual reality is the embodiment of reality, but it is not real. It is also a process of simulating scenes from a real or imaginary reality that allows learners who use it by implementing tasks and performing the required work within simulation scenes and their impacts in real time.
Yong (2000) points out that Virtual Reality Technology is a simulation of reality through the use of a hologram and fixed and animated three-dimensional objects. This is accompanied by the techniques used in motion, sound, music, graphics and backgrounds inspired by real reality in an image employed with each other to give a great impact by simulating different environments. VR BOX is an abbreviation for the word Virtual Reality Box, which is one of the wearable technologies and one of the most important accessories for smart phones. Its mission is to transfer information from the mobile phone to the processor that displays the Virtual Reality. This device consists of a piece that covers the eyes and in front of each eye there is a lens and a small screen that displays the image in 3D technology, Therefore, the eyes capture the image from each lens separately, and then the brain installs the image to look really 3D (Al Ajmi, 2021).
Virtual Reality Box are a device contains a screen that is placed on the eyes and fixed with a belt that surrounds the head. This device enters Virtual Reality data for the person who wears them to live an experience very close to reality. This device is a small part of the Virtual Reality Systems that work in an integrated manner to affect most human senses in order to create a virtual experience as close as possible to real reality (Bakr, 2021).
Abdul Rahim’s study (2022), Al-Azzazi’s study (2021), and Shaheen’s study (2021) indicate that Virtual Reality Technology enables learners to coexist in the virtual environment and benefit from it in education, based on the principle of enjoyment and observation before practice. It also creates an interactive educational atmosphere that attracts the attention of the learner to deal with the educational material in a more natural and effective manner, which facilitates this provision of the learner with audio instructions or in the form of animations that facilitate the process of integration into this environment.
Ismail and Hassanein (2001) indicated that the shooting skill that both the player and the spectator love is the one that spreads enthusiasm in the match and pushes the players to make more efforts to win. The team that the shooting players are good at has high morale and great self-confidence, and these qualities are among the most important reasons for winning. The Handball game is a game of goals, which means that the winning team shall achieve more goals than the opposing team. The skill with which the goals are scored is the shooting skill, as it determines the result of the match. Therefore, it is one of the basic and important skills in the game of Handball and the boundary between winning and losing. However, the basic skills and offensive plans of various forms become useless unless they culminate in the end with a successful shot at the goal.
The importance of using Virtual Reality Technology to benefit from it to overcome the difficulties facing teachers, develop learning methods and diversify teaching methods to suit the requirements of the era in which we live, Therefore, it is necessary to use Virtual Reality Technology that relies on a three-dimensional simulation environment that provides interaction with vision, sound, or by touch, as if it is a fictional world in teaching various sports skills (Younis and Al Shaqaifi, 2022).
Study Problem
One of the technological innovations that appeared in the educational process that affects the learner, whether in the field of sports and others, and achieves maximum success in the educational process is the programs designed with 3D technology, which is an emerging advanced educational technology that helps learners understand and comprehend information in different ways and gain experiences immediately. By reviewing previous studies in this field in the Jordanian and Arab environment, such as Ahmed’s study (2021), Al Jabali et al.’s study (2022), and Turki’s study (2020), there is no study that deals with the study of the impact of using virtual reality to learn different Handball skills, and all of these studies dealt with skills sports in other games. Through the work of the researcher as a teacher of the Handball course at the Faculty of Sports Sciences at Mutah University, the researcher noticed that there is difficulty in learning the shooting skill in the manner of explanation and the performance of a form by the teacher, which takes a longer time in the process of learning skills for learners. In the framework of the researcher keeping pace with recent progress in teaching and learning technology in the field of Handball and the using of tools and auxiliary methods in a way that ensures an optimal improvement in the performance level of learners, the idea of research came through designing a proposed educational program for virtual reality using VR BOX and identifying its impact to learn the shooting skill of Handball. Objectives of the study:
The study aims to identify the following:
1- The impact of using Virtual Reality Technology, VR BOX, to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
2- The impact of using the traditional method to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
3- The differences between the control group and the experimental group to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
Study hypotheses:
1- There are statistically significant differences at the significance level (α≤0.05) between the pre and post measurements of the control group, in favor of the post- test measurement to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
2- There are statistically significant differences at the significance level (α≤0.05) between the pre and post measurements of the experimental group and in favor of the post- test measurement to learn the shooting skill of Handball. 3- There are statistically significant differences at the level (α≤0.05) in the posttest measurement between the experimental group and the control group, in favor of the experimental group to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
Methodology
Study approach
The experimental approach with a two-way design was used using an experimental and a control group, by comparing the pre and post measurement for each group, then comparing the two groups.
Study population
The study population consisted of (54) students enrolled in the Handball course (1) at the College of Sports Sciences, Mutah University, according to the admission and registration records for the summer semester 2020/2021.
Study sample
The study sample was randomly chosen and consisted of (30) students. The study sample was divided into two groups:
Experimental group
It consisted of (15) students learning the shooting skill using virtual reality (VR BOX) for (6) weeks, with two meetings per week.
Control group
It consisted of (15) students learning the shooting skill using the traditional method for (6) weeks, with two meetings per week.
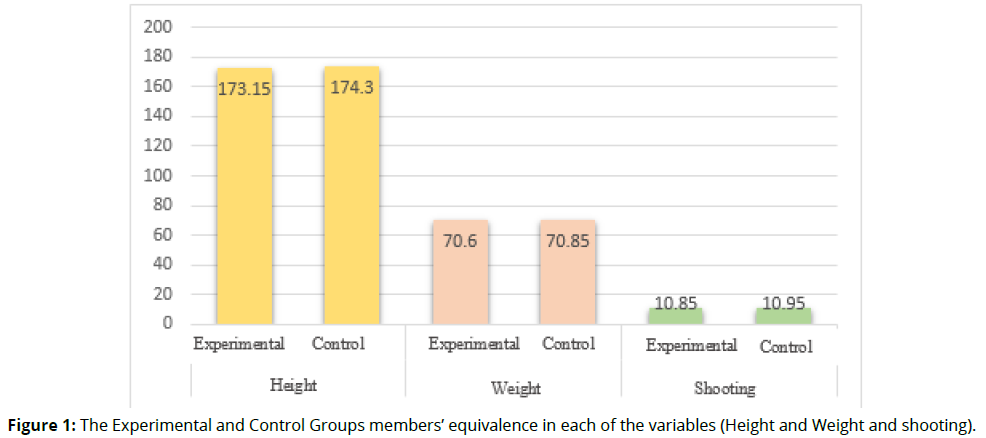
In order to verify the equivalence of the research groups (Experimental & Control Groups) in order to verify that the improvement in the research variables is due to the method of virtual reality (VR BOX) (independent variable), a set of tests was applied, represented by: (the divided the shooting at the goal), in addition to verifying the equality of the members of the (Experimental & Control Groups) in each of the variables (height and weight). The aforementioned is shown in table 1 as follows (Table 1):
It is indicated by table 1 that there are no statistically significant differences between the control and experimental groups according to height, weight, and the variables of the study, which is evidence that the members of the two groups are equal in these variables before starting the application of the program (Figure 1).
| Variable | Group | No. | Arithmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | Freedom degrees | T-Value | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height | Experimental | 15 | 173.150 | 2.621 | 38 | -1.378 | .176 |
| Control | 15 | 174.300 | 2.658 | ||||
| Weight | Experimental | 15 | 70.600 | 2.349 | 38 | -.305 | .762 |
| Control | 15 | 70.600 | 2.815 | ||||
| shooting | Experimental | 15 | 10.580 | 1.599 | 38 | -.202 | .841 |
| Control | 15 | 10.950 | 1.538 |
The pilot study
To recognize problems and errors that may occur during the study application process, the researcher conducted a survey study on (20) students, including students from the Faculty of sports sciences and students from outside the study sample, for a week with two meetings.
Educational Programs using Virtual Reality (VR box glasses)
To achieve the objectives of the study, the researcher used virtual reality (VR BOX glasses) to teach the basic shooting skill of Handball, and the researcher filmed a group of Handball players and national team players while performing the shooting skill and applied them to a set of different exercises for the skill under study in order to use video clips in preparation for the proposed educational program using virtual reality, and the VR Playe program was used, VR Video Converter, available on Google Play and is considered the best players for virtual reality and three-dimensional videos that gives you full control and supports all modes, this application plays videos from the phone's memory so you can watch all the videos recorded in virtual reality mode, VR Video Converter provides a simple user interface and easy commands so you don't need to take out your phone while watching, the virtual media player contains the latest playlist so you can easily switch to the last played video where the display screen has been divided into two similar screens, where the performance of teaching the skill of aiming through glasses Virtual reality (VR).
And then the content of the training is presented to develop the performance level of learners through the use of smart phones, and the educational content containing the technical aspects of the shooting skill is sent to learners during the educational unit and downloaded through the VR Player program and VR Video Converter, then the phone is placed inside the virtual reality glasses to view the educational content.
The actual implementation of the educational module was carried out using virtual reality technology by displaying educational content to learners through smartphones and virtual reality glasses, where a pair of glasses was equipped for each learner and an internet network inside the gym, then the teacher sends to the learners how to implement the educational module to each learner's phone and upload it to the Playe program and VR Video Converter then the phone is placed inside the glasses, and the technical aspects of the skill and the exercises are viewed with a panoramic view at an angle of 360 ° and in a holographic form and after completion of the viewing, the learners place the glasses in the designated place and then apply what has been watched and learned, and in case the learner is unable to perform the skill correctly, it is returned again to watch.
The educational program has been implemented with two meetings of 50 minutes' duration for six weeks and table 2 shows the time distribution of the educational program (Table 2).
| Warm Up | Educational Aspects | Practical Aspects | Total Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | 30 | ||
| Educational Units Number | weeks Number | Daily unit time in minutes | Time in weekly minutes | |
| 12 | 6 | 50 | 100 | 600 |
The applied exam used in the study
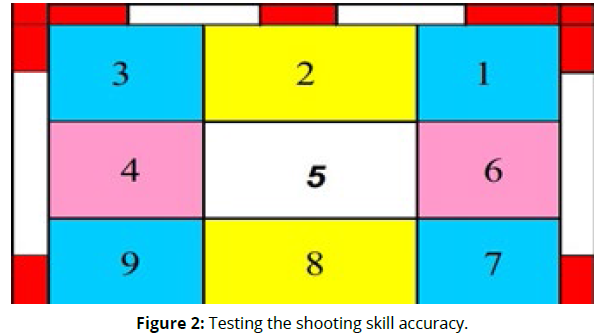
As for the test used in the study to measure the shooting skill of Handball, the tests that correspond to this skill under study have been limited by reference to scientific references that specialize in measuring in Handball (Khalil, 2014, al-Shaalan and Wadi, 2018, Al-Mansi, 2013, al-Shaalan et al., 2016) (Figure 2).
Purpose of the test: measurement of shooting skill accuracy
Tools: Handball -Throw Line - Divided Goal
Performance method: A Handball thrower divides the goal to measure the accuracy of shooting into nine rectangles and draws a line on the ground 9 m away from this figure, the player scores from behind the line with a pivot step, taking into account that the one who hits the ball (1,3,7 or 9) and its distance (1 M * 60 cm), gets 3 degrees, which represents the four angles of the goal. Whoever hits the rectangular ball 6 or 4, gets 2 degrees, which its dimensions are (1 m * 80 cm), and whoever hits the rectangular ball No. (2,5 or 8), gets 1 degree, whose dimensions are (1 m * 80 cm). Whoever hits the ball and does not score at any goal inside the corners of the goal gets zero, each player has 10 attempts.
Scientific Transactions of the Study Test
Tests validity
The researcher used apparent validity, by looking at the scientific references and previous studies that used this test (Khalil, 2014, Al-Shaalan and Al-Wedyan 2018, Al-Shaalan et al., 2016, Al-Mansi, 2013, Al-Shaalan, 2010).
Tests reliability
In order to calculate the reliability of the tests, with the aim of ensuring the scientific and statistical validity of their application to the study sample, the researcher applied the test to a sample from outside the original study sample of 15 persons, and the results of the Pearson correlation coefficient were as shown in table 3 (Table 3).
The test |
Value of Pearson Correlation Coefficient | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Testing the shooting skill accuracy | .922 | .000* |
| * Statistical function at indicative level (α≤0.05) | ||
Pearson correlation coefficient between application and re-application on a sample (N=15) for the research test, represented by:
Study variables
Independent variables:
Virtual Reality Style (VR BOX glasses)
Dependent variables:
The skill shooting performance level
Statistical methods used:
To test the validity of the study hypotheses, statistical treatments were performed using the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS), as follows:
1- Arithmetic averages
2- Standard deviations.
Presentation and Discussion of Results
The answer to the first hypothesis, which as follows:
"There are statistically significant differences at the level (α≤0.05) between the pre and post-test measurements of the control group members and in favor of the post-test measurement on learning the skill shooting in Handball."
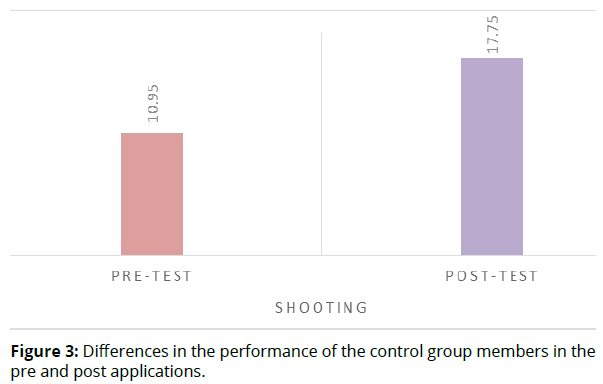
To test the validity of this hypothesis, the arithmetic means, standard deviations, and "T" value were used to clarify the differences between the pre and post applications. Table 4 shows the results of this (Table 4 & Figure 3).
Variables |
Measurement | Arithmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | Degrees of Freedom | (T) value | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shooting | pre-test | 10.95 | 1.538 | 19 | -17.228 | .000* |
| Post-test | 17.75 | 1.333 | ||||
| *Statistically significant at the level (α≤0.05). | ||||||
The data provided in table 4 show statistically significant differences at the level of significance (α≤0.05) in the value of (T) and the level of significance associated with it in the level of performance of the control group members in the shooting variable, indicating the positive effect of the traditional method, according to the researcher, the traditional method is one of the direct and fast methods of communicating information where it depends on the commanding method. The teacher controls the educational attitude and adjusts the circumstances surrounding the educational process. He or she is planning, implementing and evaluating and the learner's role is limited to implementing what is required of him or her. This opinion agrees with what he pointed out (Al-Rabeeah, 2021) that the teacher is the focus of the traditional method, where he makes all decisions from each (implementation, evaluation, planning), prepares the lesson and presents it to learners, provides templates and examples with explanation and evaluation of students, but the role of the learner is to perform, obey and follow this indicates the importance of the traditional method that it increases the effectiveness of the educational process, as the traditional method depends on the teacher in explaining and teaching mathematical skills, relying on the direct method of learning and giving instructions and immediate feedback, the teacher is the one who identifies and provides practices, activities and methods that aim to provide the learner with a set of concepts and knowledge. This result is consistent with the results of the Ahmed study (2021), which indicated the effectiveness of the traditional method to improve the level of basic skills of worn beginners, and with the results of the Abu al-Naja study (2016), which indicated the effectiveness of the traditional method to teach the shooting skill of stability with a Handball.
The answer to the second hypothesis, which as follows:
"There are statistically significant differences at the level (α≤0.05) between the pre and post-test measurements of the experimental group members and in favor of the post-test measurement on learning the skill shooting in Handball."
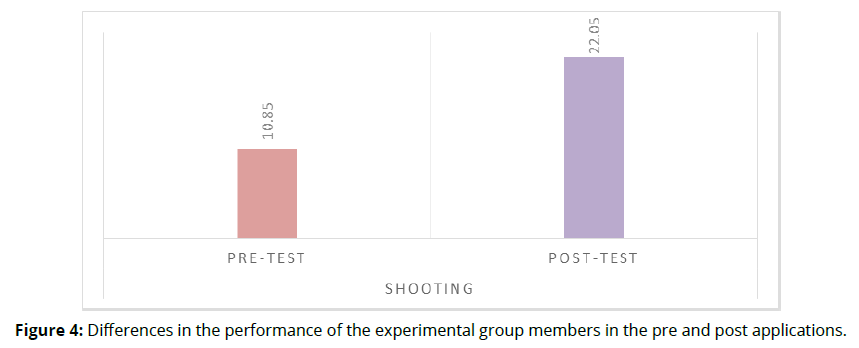
To test the validity of this hypothesis, the arithmetic means, standard deviations, and "T" value were used to clarify the differences between the pre and post applications. Table 5 shows the results of this (b and Figure 4).
Variables |
Measurement | Arithmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | Degrees of Freedom | (T) value | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shooting | pre-test | 10.85 | 1.599 | 19 | -25.874 | .000* |
| Post-test | 22.05 | 1.605 | ||||
| *Statistically significant at the level (α≤0.05). | ||||||
Data in table 5 show statistically significant differences at significance level (α≤0.05) In terms of the value of (T) and the level of indicator associated with it in the level of performance of the experimental group members in the shooting variant, which indicates the positive impact of the experimental method. The researcher attributes this improvement to the effectiveness of the virtual reality program, which was applied to this group, where the learner was provided with new approaches for the acquisition of skills in an individual manner in an appropriate sequence, with replay and retrieval of information commensurate with his individual abilities. Also, the available photos and videos give an opportunity for learners to apply and practice the shooting skill and correcting performance errors by returning to the available program again, and this leads to improving and developing skill performance, and this is what Turki (2020) pointed out that virtual reality is an advanced educational technology that helps learners understand and perceive information in different ways and gain experiences immediately, Virtual reality is a new type of education that adds a wide range of scientific analysis to individuals, the creation of a three-dimensional educational environment in which the user is active interacts with the artificial world and allows him to be surprised by the addition of the sensory perception felt by individuals in the virtual environment, and this is what Shaheen (2021) pointed out that virtual reality technology supported by three-dimensional VR BOX glasses plays an effective role in the learning process, which contributes to raising the performance level of learners, as virtual reality produces almost clear, easy-to-understand contexts as a real world and virtual reality glasses are a means that encourages learners to learn, arouses their motivation and distancing boredom from the methods prevailing in the learning process and are characterized by modernity in learning methods as well as in the use of modern-day technology. The researcher believes that virtual reality using glasses gave an opportunity for learners to watch the optimal and correct performance of the skill through watching, which combines still and moving images, sound and downloading videos in a simplified manner and with an accurate representation of the skill, which leads to an increase in the learner’s deepening and understanding of the vocabulary of motor skills, which contributes to the work on refining The motor skill as a whole, in addition to the ability of the VR glasses to display and clarify the movements of the body parts during the performance of the skill and focus on the important parts of the performance. This has the effect of continuing learning, which improves the quality and performance of learners. This result was consistent with the results of the Abdul Rahim study (2022) which indicated the improvement of the members of the experimental group in post-test measurement that used virtual reality to teach some skills on the balance beam of gymnasts, and also agreed with the results of the Shaheen study (2021) which indicated that the use of virtual reality supported by threedimensional VR BOX glasses to teach the crushing strike skill in volleyball has a positive impact on improving the members of the experimental group in posttest measurement.
The answer to the third hypothesis, which as follows:
There are statistically significant differences at the level (α≤0.05) in the post-test measurement between the experimental group and the control group, and in favor of the experimental group on learning the skill shooting in Handball."
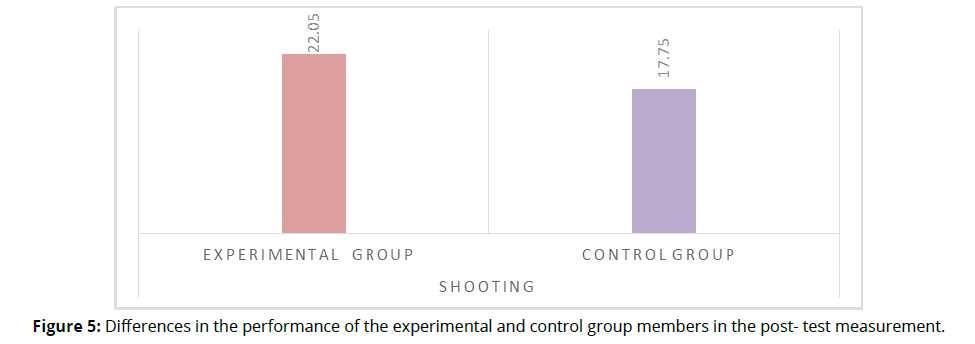
To test the validity of this hypothesis, the arithmetic means, standard deviations, and "T" value were used to clarify the differences between the experimental and control group members. Table 6 shows the results of this (Table 6 & Figure 5).
Variables |
Measurement | Arithmetic Mean | Standard Deviation | Degrees of Freedom | (T) value | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shooting | Experimental Group | 22.05 | 1.605 | 38 | 9.217 | .000* |
| Control Group | 17.75 | 1.333 | ||||
| *Statistically significant at the level (α≤0.05). | ||||||
Table 6 shows statistical differences at the significance level. (α≤0.05) Between the control and experimental groups in the post-test measurement on learning the shooting skills of Handball and in favor of the experimental group, the researcher attributes the superiority of the experimental group to the new virtual learning environment that was available to learners to create a three-dimensional fantasy environment through continuous training in the shooting skill during the periods of the educational program while presenting the technical performance of the skill and then presenting it to the learners at the beginning of the educational unit with continued application of existing exercises in virtual reality. According to the researcher, the use of VR in the educational process creates an exciting learning environment for learners and engages all the senses of learners. This is what Allam and Qutb pointed out (2022) The three-dimensional VR BOX visual thriller from different angles in the skill performance of learners When performing the skill, it retrieves the three-dimensional intellectual image displayed and internal feedback which helps correct its errors by itself if it finds that the learner achieves the highest performance rate, this result is consistent with what Mohammed and others indicated. (2020) that the use of modern technological methods in motor skills education provides the learner with the opportunity to witness the optimal performance of the skills to be learned, thereby helping to provide learners with better feedback than the traditional method of education. From the researcher's point of view, the use of VR technology enables learners to coexist in the virtual environment and benefit from it in education based on the principle of enjoyment and observation before practice. It also creates an interactive educational atmosphere that attracts the learner's attention and even immerses him in the educational material contained therein in a more natural and effective way, making it easier to provide learners with audio or animated guidance that facilitates integration into this environment, as indicated by Ahmed (2021) Virtual reality adds a wide range of imagination among learners for its ability to create a three-dimensional environment in which the user is active and interactive with the artificial world and the learner feels like a part of the learning environment during a near-complete simulation of the educational attitude, which makes There greater motivation towards learning. This result is consistent with the results of a Turki study (2022) which indicated that the members of the experimental group outperformed the control group, which used a virtual reality tutorial using VR glasses to learn the basic skills of junior football guards, and also agreed with the results of the Ajami study (2021) which indicated the superiority of members of the experimental group over the control which used a virtual reality educational program to teach some badminton skills to students of the Faculty of Sports Education.
Results
• The use of virtual reality-technology learning glasses VR BOX has contributed in a positive way to learning the shooting skill of Handball.
• Using traditional style has contributed in a positive way to learning the shooting skill of Handball.
• Members of the experimental group that used VR BOX glasses as an educational tool outperformed those of the control group that used the traditional style of learning the shooting skill of Handball.
Recommendations
• Using VR BOX glasses as one of the modern teaching methods and methods to learn the shooting skill of Handball.
• Teaching courses for sports education teachers to teach them how to use VR BOX glasses in education.
• Provide VR BOX glasses as an educational tool in sports education faculties.
References
Abdul Rahim, A. (2022). The effectiveness of virtual reality technology in the level of performance of some skills on the balance beam for gymnasts, Assiut Journal of Physical Education Sciences and Arts, p (62), c (1), 248-265.https://doi.org/10.21608/jprr.2022.259726
Abul-Naga, A, Hani, M, and Knawi, R. (2016) The effect of an educational program using the blended method on learning the shooting skill of jumping and cognitive achievement in handball for students of the Faculty of Physical Education at the University of Karbala, Scientific Journal of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, p. (26), 125-146.https://doi.org/10.21608/ejsk.2016.95474
Ahmed., Y. (2021). A proposed educational program using virtual reality glasses at the level of performing some basic skills for ballet beginners. Journal of Comprehensive Education Research, (8) 17, 342-358.https://doi.org/10.21608/jsei.2022.221633
Al-Ajami, p. (2021). The effect of an educational program using virtual reality on teaching some badminton skills to students of the Faculty of Physical Education. Assiut Journal of Physical Education Sciences and Arts, 56 (2). 410-433https://doi.org/10.21608/jprr.2021.173732
Al-Azazy, M. (2021). The effect of virtual reality technology on learning the long jump for high school students in Zagazig, Physical Education Research Journal, No. (69), No. (133), 131-151.https://doi.org/10.21608/mbtr.2021.93951.1054
Allam, A, and Kotb, A. (2022). The effect of training using virtual reality technology on the development of some basic skills for judokas. Journal of Sports Science Applications, (8) 114, 169-203.https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/jaar.2022.283873
Al-Mansi, T. (2013) Building standard levels for some physical and skill elements and physical measurements for selecting girls for promising handball centers in Jordan, Mutah Journal for Research and Studies, Volume 28, Number 1.
Al-Shaalan, M., and Al-Wedyan, M. (2018). Finding Standard Scores for Some Handball Skills for Students of the College of Sports Sciences at Mutah University, An-Najah University Journal for Research - Human Sciences, Vol. (32), p. (10), 1953-1973.https://journals.najah.edu/journal/anujr-b/issue/anujr-b-v32-i10/article/1530/
Al-Shaalan, M. (2010). The effect of the self-learning method using the computer for people with multiple intelligences on the performance level of the passing and shooting skills in handball, PhD thesis, University of Jordan, Jordan.
Al-Shaalan, M., Al-Khattbeh, M., Al-Raba’a, J. (2016) Handball skills, 1st edition, Amman: Knowledge Treasures House
Baker, C. (2021). The effect of using virtual reality glasses on learning to swim on the back crawl, master's thesis, Sadat University, Egypt.
El-Gebali, M., Mostafa, A., Safwat, P., Tarek, S. (2022). The effect of an educational program using virtual reality technology in developing some basic skills in belly crawl swimming for beginners. Scientific Journal of Physical Education and Sport Sciences. Helwan University, (96) 3, 355-374.https://doi.org/10.21608/jsbsh.2022.156253.2212
Ismail, K, and Hassanein, M (2001) The Modern Handball Quartet, Al-Kitab Center for Publishing, first edition Makransky, G., & Petersen, G. B. (2021). The cognitive affective model of immersive learning (CAMIL): A theoretical research-based model of learning in immersive virtual reality. Educational Psychology Review. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1007/s10648-020-09586-2
Khalil, M. (2014). The effect of exercises for a miniature and regular playground in teaching some basic handball skills and retaining them for sixth graders, master's thesis, Diyala University, Iraq.
Mikropoulos, T. A., & Natsis, A. (2011). Educational virtual environments: A ten-year review of empirical research (1999–2009). Computers & education, 56(3), 769-780.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.10.020
Mohamed A. St., Ahmed, St., Farag, M, Jamal, P, Amir, P. (2020). The effect of using virtual reality glasses on learning some basic skills among buds in volleyball. Scientific Journal of Physical Education and Sport Sciences, 24(7), 17-34.https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/sjes.2020.261400
Plancher, G., Nicolas, S., & Piolino, P. (2008). Contribution of virtual reality to neuropsychology of memory: study in aging. Psychologie & neuropsychiatrie du vieillissement, 6(1), 7-22
https://www.jle.com/10.1684/pnv.2008.0119
Rabia, J. (2021). The use of the imperative, binary and comprehensive method to learn the skill of serving in volleyball among Taibah University students, Journal of Education, Al-Azhar University, M (40), p. (191), 481-506.https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/jsrep.2021.189841
Shaheen, A. (2021). The effect of using virtual reality technology supported by 3D VR BOX glasses on learning the crushing hitting skill in volleyball. Scientific Journal of Physical Education and Sport Sciences. Helwan University, (92) 3, 112-148.https://doi.org/10.21608/jsbsh.2021.83778.1768
Turki, M. (2020). The effectiveness of virtual reality technology using Google VR glasses to learn some basic skills for junior soccer goalkeepers. Assiut Journal of the Arts and Sciences of Physical Education, (2) 55, 442 - 465.https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/jprr.2020.159727
Young, J. R. (2000). Virtual Reality on a Desktop Hailed as New Tool in Distance Education. Chronicle of Higher Education, 47(6).
Yunus, N., Al-Ali, A. (2022). The effect of training using virtual reality and augmented reality through the Cospaces Edu platform on the science operations skills of kindergarten students. Journal of the Faculty of Education (Assiut), (5) 38, 268-337.https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/mfes.2022.257525